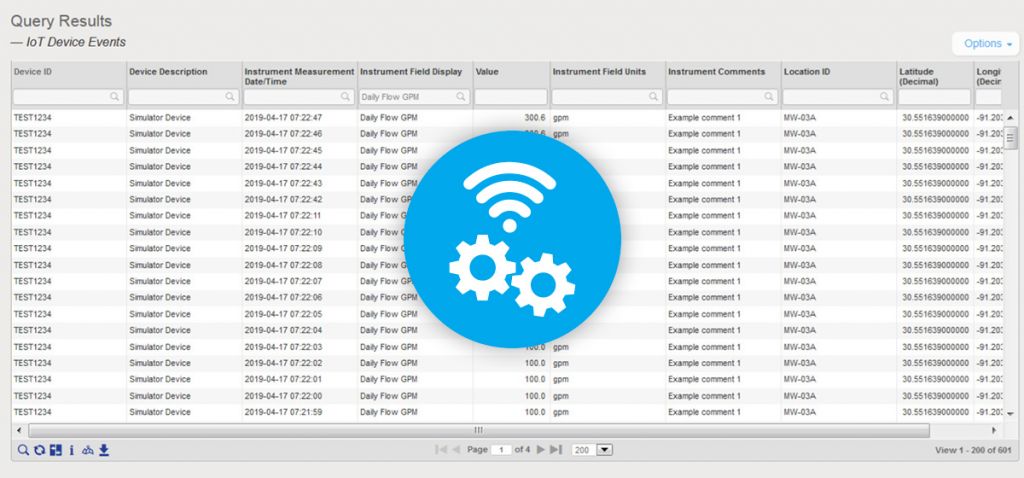
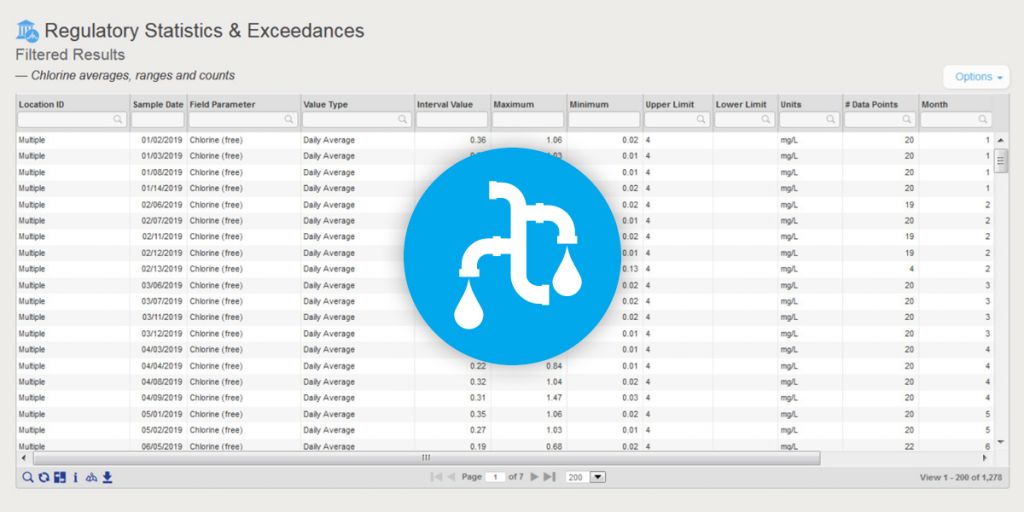
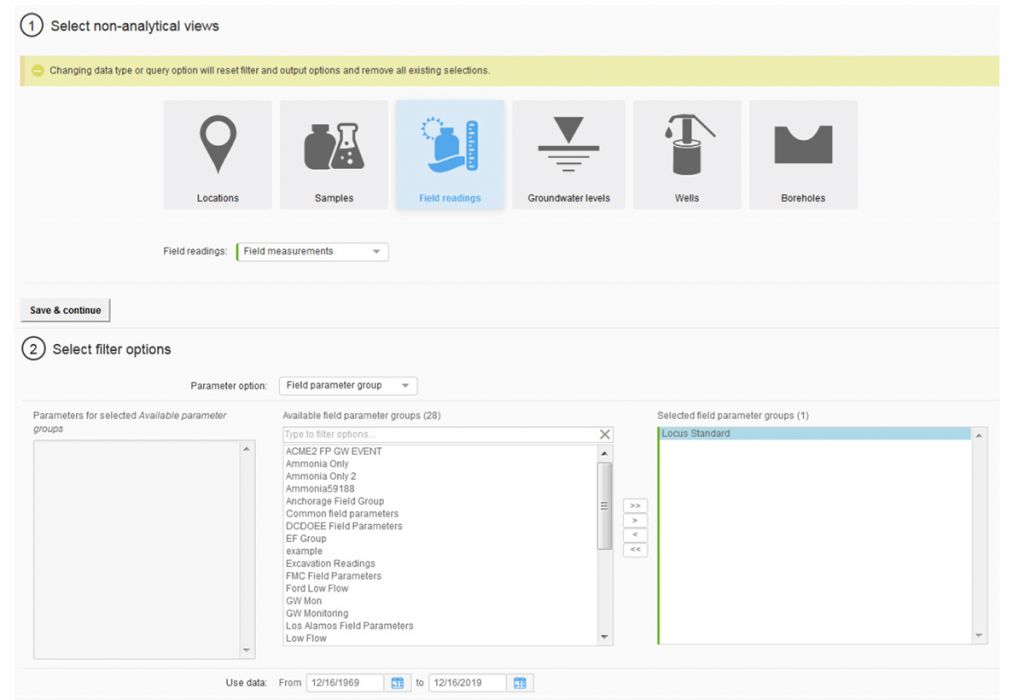
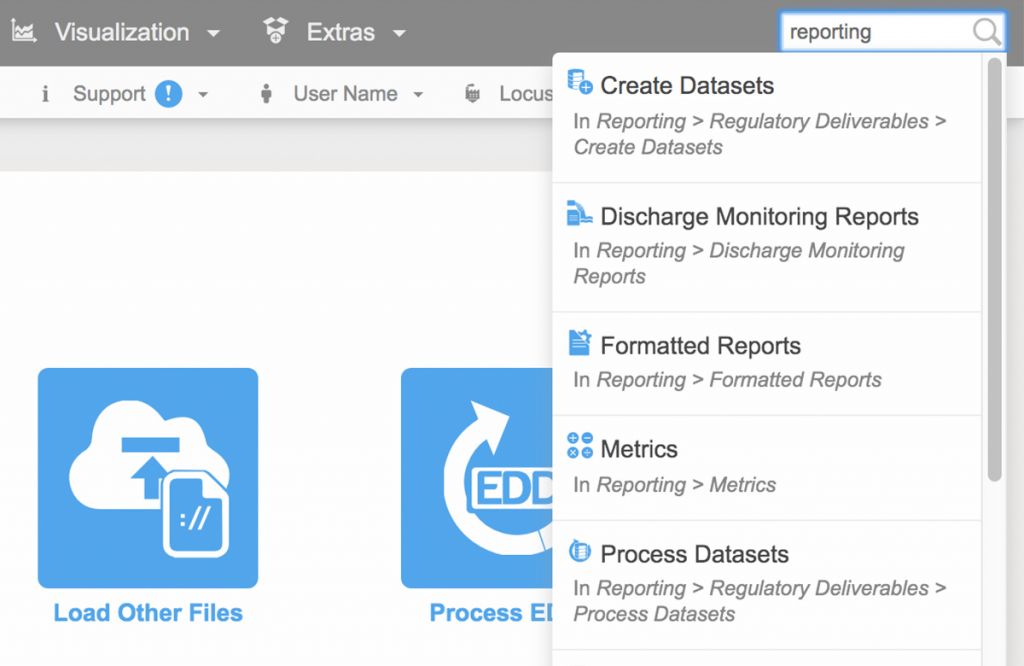
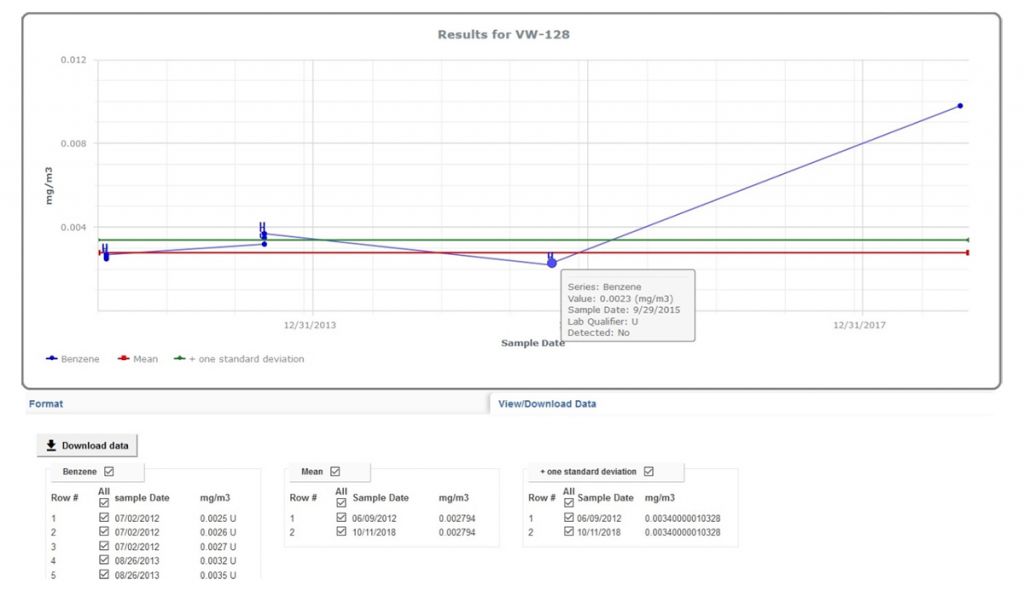
How to Prepare for EPA’s Latest UCMR 5 Guidelines
Attention all water providers: the EPA’s UCMR 5 list includes 30 contaminants (29 PFAS and lithium) that both small and large water systems have to test for and report. Can your current environmental solution handle it?
Locus EIM environmental software can handle new chemicals and analyses seamlessly. Both the standard Locus EIM configuration and the Locus EIM Water configuration (specially tailored to water utilities) are built with ever-changing regulations in mind.
We’ve put together some helpful background and tips for water providers preparing for UCMR 5 monitoring.
What water providers need to know
- The fifth and latest list (UCMR 5) was published on March 11, 2021, and includes 30 new chemical contaminants that must be monitored between 2023 and 2025 using specified analytical methods.
- SDWA now requires that UCMR include all large PWSs (serving >10,000 people), all PWSs serving between 3,300 and 10,000 people, and a representative sample of PWSs serving fewer than 3,300 people.
- Large systems must pay for their own testing, and US EPA will pay for analytical costs for small systems.
- Labs must receive EPA UCMR approval to conduct analyses on UCMR 5 contaminants.

[sc_icon icon=”download” shape=”square” size=”small” link=”https://www.locustec.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/locus_infographic_ucmr5.jpg” link_target=”_self”] Download Infographic
What’s the UCMR and why are some contaminants unregulated?
In 1996, Congress amended the Safe Drinking Water Act with the Unregulated Contaminant Monitoring Rule (UCMR). Under this new rule, US EPA can require water providers to monitor and collect data for contaminants that may be in drinking water but don’t have any health-based standards set (yet) under the SDWA.
More than 150,000 public water systems are subject to the SDWA regulations. US EPA, states, tribes, water systems, and the public all work together to protect the water supply from an ever-growing list of contaminants.
However, under the UCMR, US EPA is restricted to issuing a new list every five years of no more than 30 unregulated contaminants to be monitored by water providers.
This helps reduce the burden on water providers, since monitoring and testing for the existing long list of regulated contaminants already requires a significant investment of time and resources.
Throughout the course of this monitoring, US EPA can determine whether the contaminants need to be officially enforced— but this would require regulatory action, routed through the normal legislative process.
Tips for managing UCMR in 
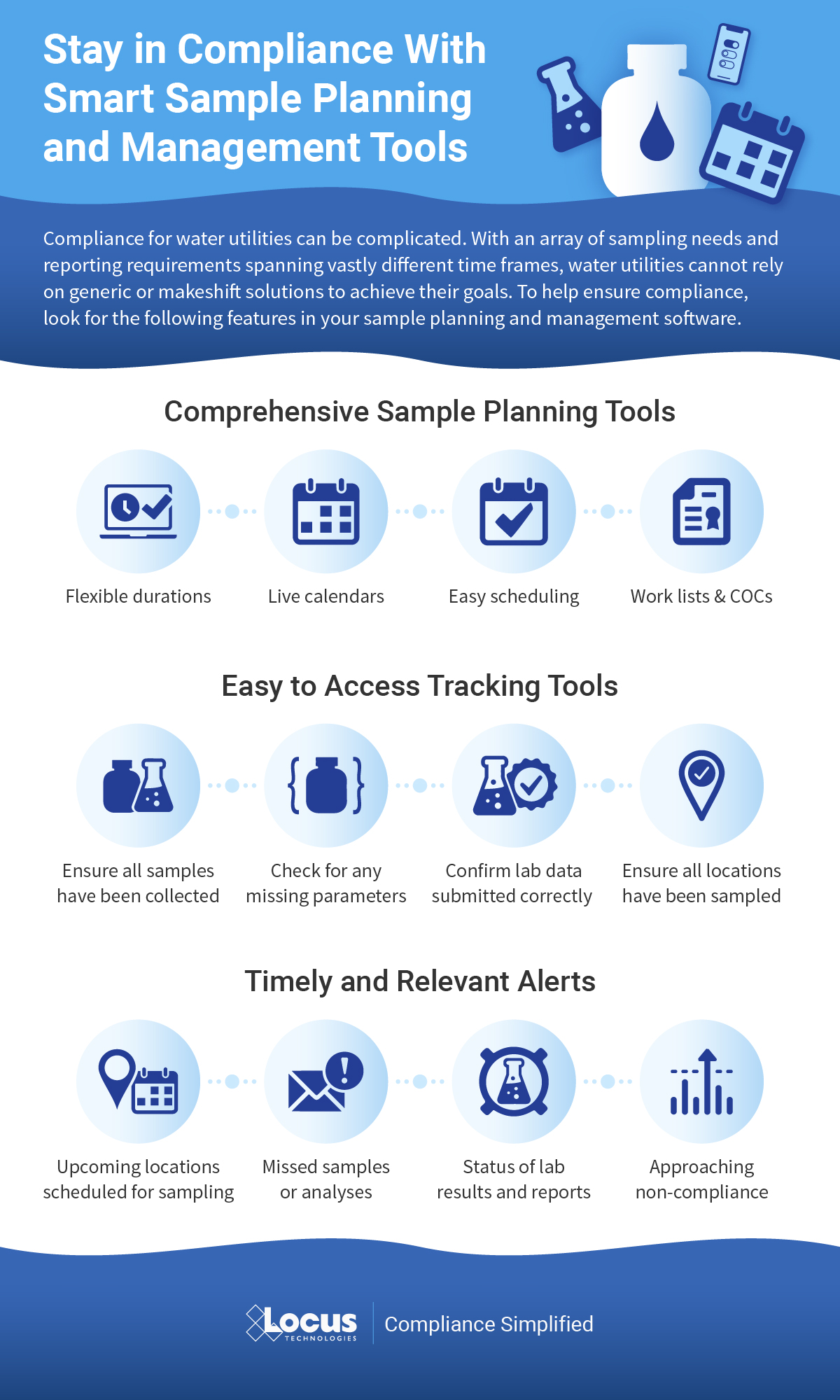
- DO use EIM’s Sample Planning module to set your sample collection schedule ahead of time, as requirements vary and are on specific schedules
- DO take advantage of EIM’s sample program features to track and manage UCMR data, or consider using a dedicated location group to track results, keeping them separate and easy to find for CCR reporting.
- DON’T worry about adding in new analytical parameters in advance. With EIM’s EDD loader, you can automatically add them when the data arrive from the laboratory.
Contact your Locus Account Manager for help setting up your EIM database in advance of your sampling schedule, and we’ll make sure you’re equipped for UCMR 5!
Not yet a customer? Send us a quick note to schedule a call or a demo to find out how Locus software can completely streamline your water sampling and reporting.
[sc_button link=”#eimquote” text=”Get a demo of Locus EIM” link_target=”_self” centered=”1″]
More helpful links:
- Locus adds Consumer Confidence Report (CCR) module to Locus EIM Water
- Improving arsenic detection and keeping it out of drinking water
- Making water quality data more transparent: Lessons from an annual water quality report
- Water quality data management: 10 best practices
[sc_fullwidth background_image=”15039″ background_style=”cover” background_position_horizontal=”center” background_position_vertical=”top” video_background_acpect_ratio=”16:9″ container=”1″]
Get a demo
[/sc_fullwidth]