Create Your Own Apps on our Sustainability and EHS Compliance Software Platform
We engineered Locus Platform to empower users to conceive and create their own apps on our EHS Compliance Software Platform.
We engineered Locus Platform to empower users to conceive and create their own apps on our EHS Compliance Software Platform.
Locus enables power users to tweak the software to make it their own without writing a line of code or talking to a single person.
In today’s world, businesses across various industries face the challenge of managing and reporting environmental data efficiently.
When looking for a GHG reporting program, there is one element that is typically overlooked. This short video gives us more insight.
For the last 25 years, Locus has synthesized knowledge of environmental science with a vision for effectively gathering, aggregating, visualizing, and analyzing emissions of all sorts and environmental data. This work aims to help organizations marshal their environmental data to manage better and, where possible, reduce their environmental footprints.
This approach has differed from many other environmental software startups that have come and gone in the past ten years. Locus’ distinction comes from harnessing the true multitenant Cloud and a unique perspective on how to address the complex issues of environmental information management. Cloud technology offers Locus customers numerous advantages: Improved data collection,
aggregation, visualization, business analytics, and analysis, and the cost reduction inherent in web-based software all translate into a competitive advantage and increased customer profitability.
So, rather than “one software solution per problem,” Locus has built an enterprise-scale software solution tailored to meet all customer’s needs in a single SaaS platform. This approach eliminates redundancy and incompatibility issues with other enterprise-management systems, giving organizations unprecedented control over their data. As the industry evolves and new markets continue to grow, Locus is positioned to grow with them, staying at the forefront of environmental and sustainability information management and promoting a vision of collaborative global stewardship.
And that global stewardship is where Locus would like to see environmental data management have a more significant impact on policy, mitigation efforts, and understanding the complete picture of how human activities affect the planet.
Locus is not just selling software to address an evolving regulatory landscape (which is why most customers are looking for environmental compliance software) but also because there is an underlying urgency to tackle what the Locus team views—along with many other scientists—as a climate and environmental crisis. The 21st century’s environmental challenges include shortages of drinkable water; the impact of various pollutants that enter our atmosphere; the strains of our ever-increasing population on limited resources and threatened ecosystems; and climate change causing extreme weather conditions that push more and more the world’s population into precariousness.
We need a collective and holistic understanding of the problems we face. The only way to understand the whole picture and act meaningfully globally is for all of us to share the data we gather about our activities. It’s impossible to mitigate the risks and effects of our actions on the planet when we don’t have the data to characterize the problem and see a complete picture of what we face.
This complete picture will require us to monitor and collect an unprecedented quantity of data, and it’s with this massive data explosion, Locus’s vision comes into play. To achieve this end, organizations in the private and public sectors will need to track and upload their environmental data; subsequently, these data need to be made available through an interconnected database for environmental data management so that scientists and others can collectively view the results of our activities and act on a grander scale.
Getting to the point of sharing all of these data is an important stretch goal right now, but it’s the direction Locus hopes to see environmental data management move in the future. In the meantime, Locus is working to support organizations of all sizes to gather their data, understand it better, and act on their analyses to improve their environmental footprints.
This is the seventh post highlighting the evolution of Locus Technologies over the past 25 years. The previous post can be found here. This series continues with Locus at 25 Years: Climate Change Software, A Generational Opportunity.
In a Software as a Service (SaaS) delivery model, service uptime is vital for several reasons. Besides the obvious of having access to the service over the internet at any given time and staying connected to it 24/7/365, there are additional reasons why service uptime is essential. One of them is quickly verifying the vendor’s software architecture and how it fits the web.
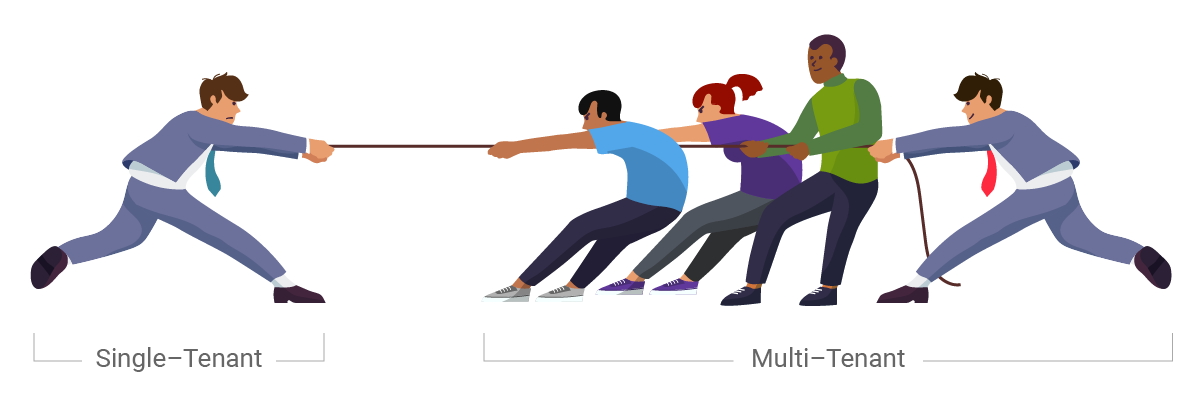
Locus is committed to achieving and maintaining the trust of our customers. Integral to this mission is providing a robust compliance program that carefully considers data protection matters across our cloud services and service uptime. After security, service uptime and multitenancy at Locus come as a standard and, for the last 25 years, have been the three most essential pillars for delivering our cloud software. Our real-time status monitoring (ran by an independent provider of web monitoring services) provides transparency around service availability and performance for Locus’ ESG and EHS compliance SaaS products. Earlier I discussed the importance of multitenancy in detail. In this article, I will cover the importance of service uptime as one measure to determine if the software vendor is running genuine multitenant software or not.
If your software vendor cannot share uptime statistics across all customers in real-time, they most likely do not run on a multitenant SaaS platform. One of the benefits of SaaS multitenancy (that is frequently overlooked during the customer software selection process) is that all customers are on the same instance and version of the software at all times. For that reason, there is no versioning of software applications. Did you ever see a version number for Google’s or Amazon’s software? Yet they serve millions of users simultaneously and constantly get upgraded. This is because multitenant software typically provides a rolling upgrade program: incremental and continuous improvements. It is an entirely new architectural approach to software delivery and maintenance model that frees customers from the tyranny of frequent and costly upgrades and upsell from greedy vendors. Companies have to develop applications from the ground up for multitenancy, and the good thing is that they cannot fake it. Let’s take a deeper dive into multitenancy.
An actual multitenant software provider can publish its software uptime across all customers in real-time. Locus, for example, has been publishing its service uptime in real-time across all customers since 2009. Locus’s track record speaks for itself: Locus Platform and EIM have a proven 99.9+ percent uptime record for years. To ensure maximum uptime and continuous availability, Locus provides redundant data protection and the most advanced facilities protection available, along with a complete data recovery plan. This is not possible with single-tenant applications as each customer has its software instance and probably a different version. One or a few customers may be down, others up, but one cannot generally aggregate software uptime in any meaningful way. The fastest way to find if the software vendor offers multitenant SaaS or is faking it is to check if they publish online, in real-time, their applications uptime, usually delivered via an independent third party.
Legacy client-server or single-tenant software cannot qualify for multitenancy, nor can it publish vendor’s uptime across all customers. Let’s take a look at definitions:
Single-Tenant – A single instance of the software and supporting infrastructure serves a single customer. With single-tenancy, each customer has their independent database and instance of the software. Essentially, there is no sharing happening with this option.
Multitenant – Multitenancy means that a single instance of the software and its supporting infrastructure serves multiple customers. Each customer shares the software application and also shares a single database. Each tenant’s data is isolated and remains invisible to other tenants.

A multitenant SaaS provider’s resources are focused on maintaining a single, current (and only) version of the software platform rather than being spread out in an attempt to support multiple software versions for customers. If a provider isn’t using multitenancy, it may be hosting thousands of single-tenant customer implementations. Trying to maintain that is too costly for the vendor, and sooner or later, those costs become the customers’ costs.
A vendor invested in on-premise, hosted, and hybrid models cannot commit to providing all the benefits of an actual SaaS model due to conflicting revenue models. Their resources will be spread thin, supporting multiple software versions rather than driving SaaS innovation. Additionally, suppose the vendor makes most of their revenue selling on-premise software. In that case, it is difficult for them to fully commit to a proper SaaS solution since most of their resources support the on-premise software. In summary, a vendor is either multitenant or not – there is nothing in between. If they have a single application installed on-premise of customer or single-tenant cloud, they do not qualify to be called multitenant SaaS.
Before you engage future vendors for your enterprise ESG reporting or EHS compliance software, assuming you already decided to go with a SaaS solution, ask this simple question:
Can you share your software uptime across ALL your customers in real-time? If the answer is no, pass.
And if the vendor suddenly introduces a “multitenant” model (after selling an on-premises or single-tenant software version for 10+ years), who in the world would want to migrate to that experimental cloud without putting the contract out to bid to explore a switch to well established and market-tested actual multitenant providers? The first-mover advantage of multitenancy is a considerable advantage for any vendor. Still not convinced? Let me offer a simple analogy to drive home the point as to why service uptime and multitenancy matter: Tesla vs. Edison–War of Currents.
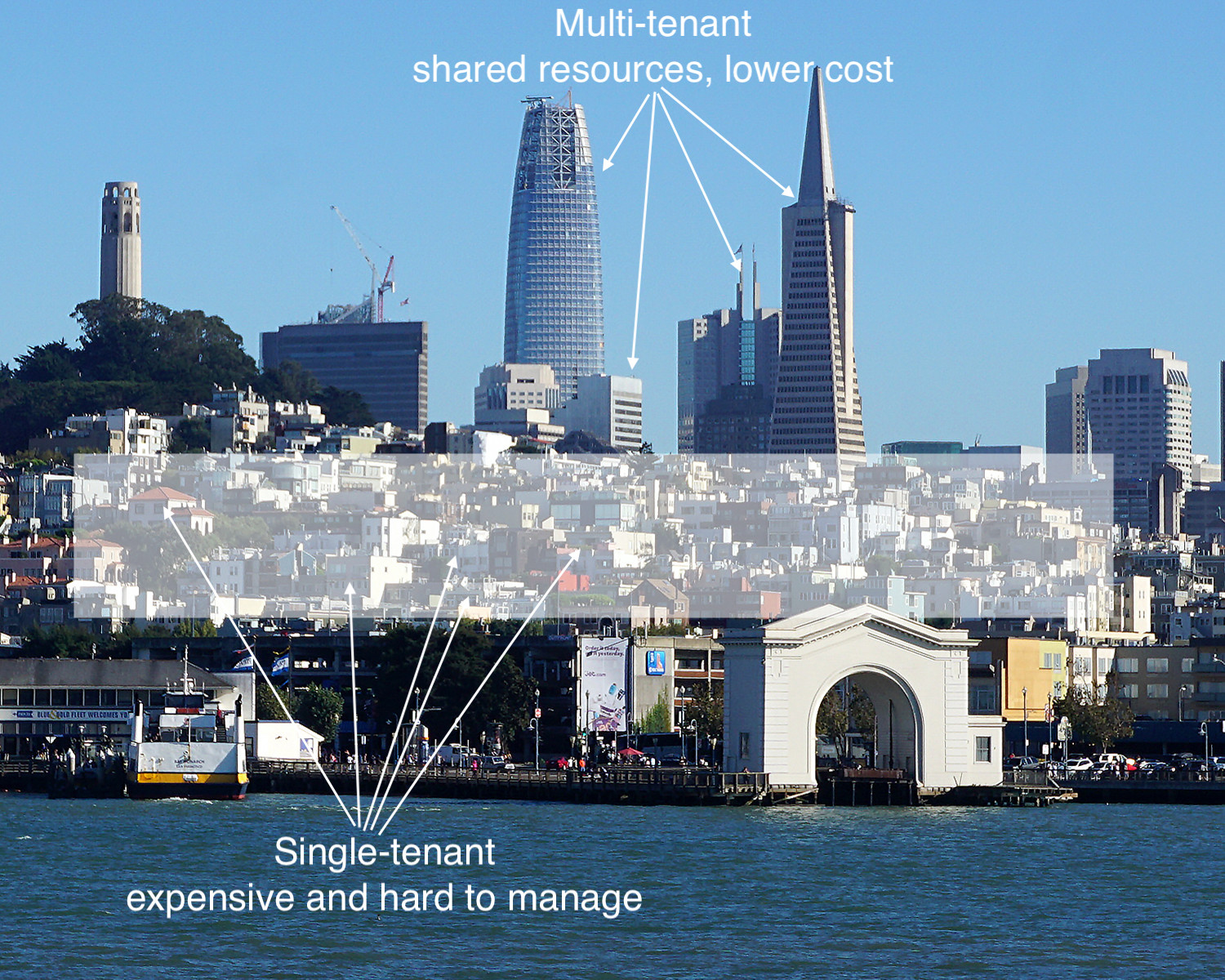

The War of Currents was a series of events surrounding the introduction of competing electric power transmission systems in the late 1880s and early 1890s that pitted companies against one another and involved a debate over the cost and convenience of electricity generation and distribution systems, electrical safety, and a media/propaganda campaign, with the leading players being the direct current (DC) based on the Thomas Edison Electric Light Company and the supporters of alternating current (AC) based on Nikola Tesla’s inventions backed by Westinghouse.
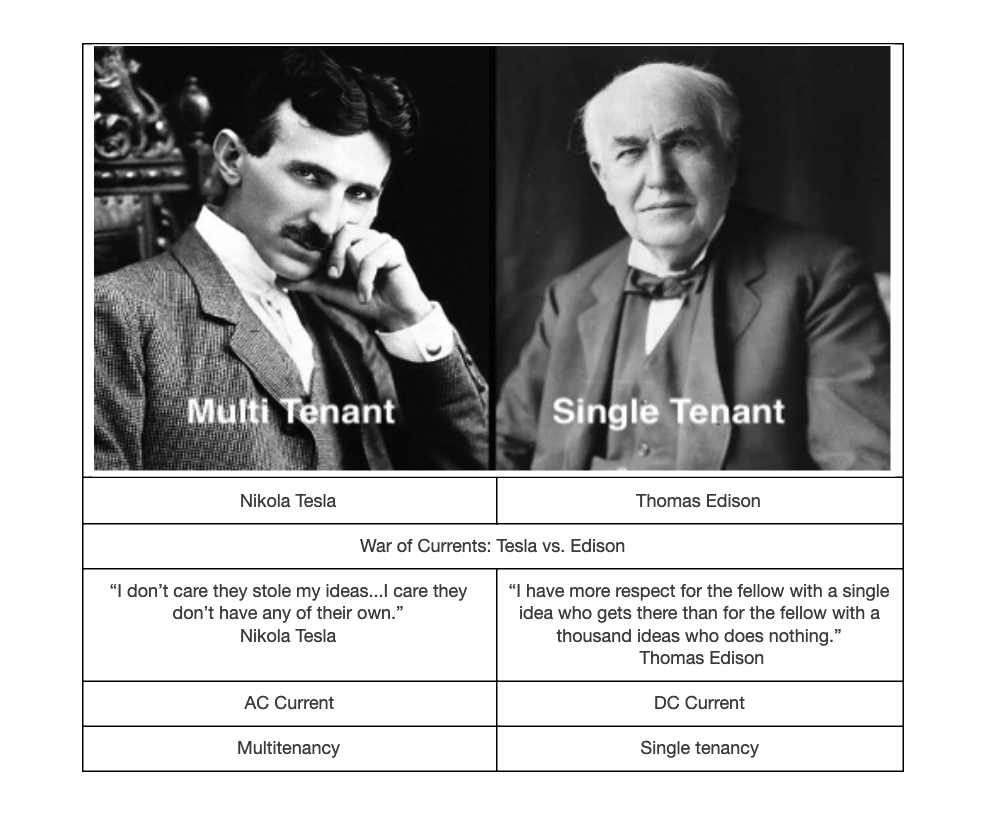
With electricity supplies in their infancy, much depended on choosing the right technology to power homes and businesses across the country. The Edison-led group argued for DC current that required a power generating station every few city blocks (single-tenant model). In contrast, the AC group advocated for a centralized generation with transmission lines that could move electricity great distances with minimal loss (multitenant model).
The lower cost of AC power distribution and fewer generating stations eventually prevailed. Multitenancy is equivalent to AC regarding cost, convenience, and network effect. You can read more about how this analogy relates to SaaS in the book by Nicholas Carr, “Big Switch.” It’s the best read so far about the significance of the shift to multitenant cloud computing. Unfortunately, the ESG/EHS software industry has lagged in adopting multitenancy.
Given these fundamental differences between different modes of delivering software as a service, it is clear that the future lies with the multitenant model.
Whether all customer data is in one or multiple databases is of no consequence to the customer. For those arguing against it, it is like an assertion that companies “do not want to put all their money into the same bank account as their competitors,” when what those companies are doing is putting their money into different accounts at the same bank.
When customers of a financial institution share what does not need to be partitioned—for example, the transactional logic and the database maintenance tools, security, and physical infrastructure and insurance offered by a major financial institution—then they enjoy advantages of security, capacity, consistency, and reliability that would not be affordably deliverable in isolated parallel systems.
Locus has implemented procedures designed to ensure that customer data is processed only as instructed by the customer throughout the entire chain of processing activities by Locus and its subprocessors. Amazon Web Services, Inc. (“AWS”) provides the infrastructure used by Locus to host or process customer data. Locus hosts its SaaS on AWS using a multitenant architecture designed to segregate and restrict customer data access based on business needs. The architecture provides an effective logical data separation for different customers via customer-specific “Organization IDs” and allows customer and user role-based access privileges. The customer interaction with Locus services is operated in an architecture providing logical data separation for different customers via customer-specific accounts. Additional data segregation ensures separate environments for various functions, especially testing and production.
Multitenancy yields a compelling combination of efficiency and capability in enterprise cloud applications and cloud application platforms without sacrificing flexibility or governance.
I love the article by Geoffrey Moore on the power of software as a service (SaaS) business model published on LinkedIn. In SaaS’s Real Triumph he writes: “by far the greatest contribution of SaaS is to free the enterprise from the tyranny of the product release model.”
He cites the operational burden, enterprise-wide distraction and associated cost to roll out an enterprise software and then the subsequent hesitation to repeat that when a new release of that software becomes available as that deployment model is not sustainable nor affordable. Companies spend big dollars buying and then deploying EHS software that they know will be outdated in just a few years. Only IT personnel benefits from that model as it may extend their employment for a few years before IT department goes out of business for good. Moore points out the painful truth, stating: “you have paid maintenance of 18 to 20% per year for anywhere from five to ten years for the express purpose of not availing yourself of the innovation created during that time period.”
Probably the main benefit of SaaS multi-tenancy (that is frequently overlooked during the software selection process) is no software versioning. This is because multi-tenant software typically provides a rolling upgrade program: incremental and continuous improvements. It is an entirely new architectural approach to software delivery and maintenance model. Companies have to develop applications from the ground up for multi-tenancy. Legacy client-server or single-tenant software cannot qualify for multi-tenancy. Let’s take a look at definitions:
Single-Tenant – A single instance of the software and supporting infrastructure serves a single customer. With single-tenancy, each customer has his or her own independent database and instance of the software. Essentially, there is no sharing happening with this option.
Multi-Tenant – Multi-tenancy means that a single instance of the software and its supporting infrastructure serves multiple customers. Each customer shares the software application and also shares a single database. Each tenant’s data is isolated and remains invisible to other tenants.
The multi-tenant architecture provides lower costs through economies of scale: With multi-tenancy, scaling has far fewer infrastructure implications than with a single-tenancy-hosted solution because new customers get access to the same software.
Shared infrastructure leads to lower costs: SaaS allows companies of all sizes to share infrastructure costs. Not having to provision or manage any infrastructure or software above and beyond internal resources enables businesses to focus on everyday tasks.
Ongoing maintenance and updates: Customers don’t need to pay costly upgrades to get new features or functionality.
Configuration can be done while leaving the underlying codebase unchanged: Single-tenant-hosted solutions are often customized, requiring changes to an application’s code. This customization can be costly and can make upgrades expensive and time-consuming because the upgrade might not be compatible with customers changes to the earlier software version.
Multi-tenant solutions are designed to be highly configurable so that businesses can make the application perform the way they want. There is no changing the code or data structure, making the upgrade process easy.
Multi-tenancy ensures that every customer is on the same version of the software. As a result, no customer is left behind when the software is updated to include new features and innovations. A single software version also creates a unique sense of community where customers and partners share knowledge, resources, and learning. Smart managers work with their peers and learn from them and what they are doing. A multi-tenant SaaS provider’s resources are focused on maintaining a single, current (and only) version of the application, rather than spread out in an attempt to support multiple software versions for customers. If a provider isn’t using multi-tenancy, it may be hosting thousands of single-tenant customer implementations. Trying to maintain that is too costly for the vendor, and those costs, sooner or later, become the customers’ costs.
A vendor who is invested in on-premise, hosted, and hybrid models cannot commit to providing all the benefits of a true SaaS model due to conflicting revenue models. Their resources are going to be spread thin, supporting multiple versions rather than driving innovation. Additionally, if the vendor makes the majority of their revenue selling on-premise software, it is difficult for them to fully commit to a true SaaS solution since the majority of their resources are allocated to supporting the on-premise software.
Before you engage future vendors for your enterprise EHS software, assuming you already decided to go with SaaS solution, ask these questions:
If the answer is yes to any of these two questions, you should not consider that vendor as they are not true multi-tenant SaaS. You should not select that vendor if they answer “we are in the process of switching to multi-tenancy.” Multi-tenancy train departed a long time ago, and no EHS vendor who is single-tenant is not going to make that switch in time to make it work.
And if they suddenly introduce a “multi-tenant” model (after selling an on-premises version for 10+ years) who in the world would want to migrate to that experimental cloud without putting the contract out to bid to explore a switch to well established and market-tested true multi-tenant providers? The first-mover advantage when it comes to multi-tenancy is a huge advantage for any vendor.

The announcements by several EHS software vendors this Fall caught my attention. After offering their software on-premisses for over a decade, suddenly many are discovering and planning to introduce multi-tenant Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) while promising to continue to maintain their current on-premises or single tenant offerings. In essence, they are introducing multi-tenancy as if it were a new version of their software. This plan is not going to work! Let me explain why.
Most public announcements begin something like this: In the next several years we plan to expand our software offerings and offer our customers the option to move from their current on-premises solution to the cloud. However, is this even possible? What they consider the “cloud” may not be a true multi-tenant cloud. That train departed years ago, and most of the current EHS software vendors missed it. While multi-tenancy has been a game changer in the tech industry, many are uncertain of exactly what makes an application “multi-tenant” or why it matters.

There is a considerable degree of (intended) confusion in the EHS software space when it comes to the definition of a real cloud or better said, multi-tenancy. Companies that are considering SaaS solutions for EHS software hear all sorts of things from EHS software vendors hoping to tap into the momentum of cloud computing. Many go as far as saying “sure; we can do multi-tenant, single-tenant, whatever tenant you need!” –anything to win the job. These vendors do not understand the real cloud.
Multi-tenancy is a significant shift in computing and requires an all-new approach to the software architecture and the delivery model from the ground up. It is transformational, and customers who intend to buy the next generation of EHS software should spend the time to understand the differences. More importantly, multi-tenancy is a principle, not a software version or an upgrade. It is not an evolutionary step; instead, it is a revolution in the software delivery model and it matters in the long run for the customer.

Figure 1: The single-tenant model cannot easily be switched or “upgraded” to multi-tenant. The software architecture does not allow it for easy switch the same way as single family home cannot be “remodeled” to become a multi-tenant highrise. What differentiates multi-tenant application architecture is its effectiveness in achieving the same goal in a scalable and sustainable fashion.
Can anyone imagine companies like eBay, Salesforce, Google, Workday, or Amazon offering a “single-tenant” solution side by side to their multi-tenant clouds? I argue that any EHS software vendor who offers a single-tenant solution of any type, cannot be a serious contender in multi-tenant SaaS.
EHS software vendors with on-premise software applications or single-tenant web-enabled offerings are seduced by the seemingly low barriers to entry into the SaaS market with an architecture that leverages virtualization. This approach allows a software company to quickly offer subscription-based services of their legacy product to their initial customers. In the long run, however, this multi-instance approach just won’t scale economically. A recent wave of ownership change of EHS software companies is the best indicator that sold companies became victims of their initial success. A SaaS provider who leverages virtualization puts the long-term viability of the business at risk as more efficient SaaS competitors come to dominate the market.
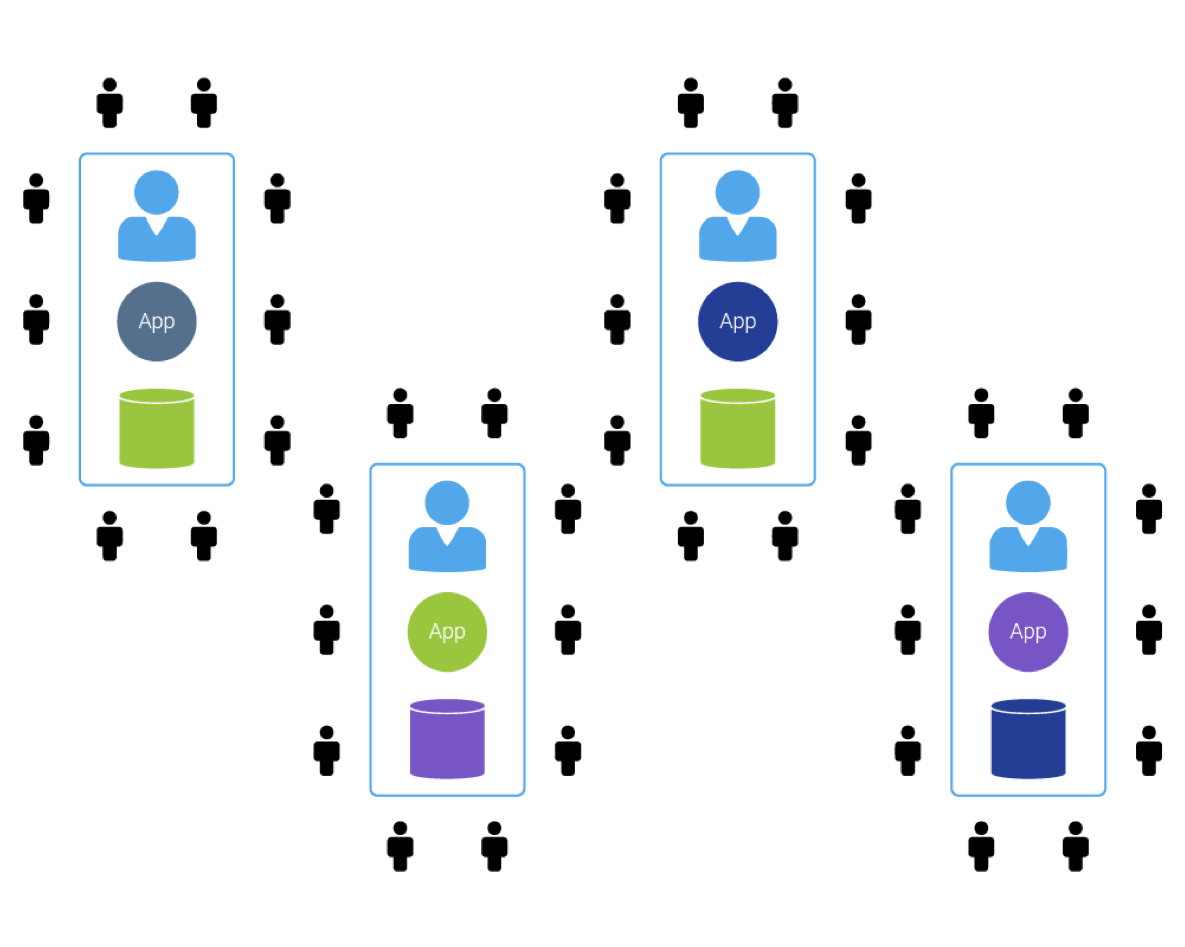
Figure 2: Single-tenant requires many more vendor resources. The resource costs are eventually passed to customers. Each upgrade of the application will require each customer to upgrade independently and the ability to implement tenant management tools and tenant-specific customizations is significantly limited. The benefit of multi-tenancy is that instead of 100 copies of the OS, 100 copies of the database, and 100 copies of apps, it has 1 OS, 1 DB and 1 app on the server with significantly less vendor resources required to manage it. And it is those savings that are on a long term passed to customers.
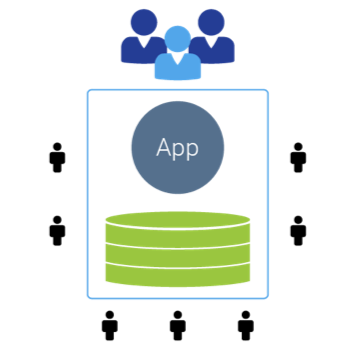
Figure 3: Multi-tenant model requires less resources and easier (and rolling) upgrades (i.e. no version number necessary). Only one software instance and hardware stack for multiple tenants. All customers are always on the latest version of software. Locus Technologies figured this out in 1999. And they contribute their phenomenal success since then exactly to the multi-tenancy. They could scale up infinitely without adding proportional cost. Others cannot.
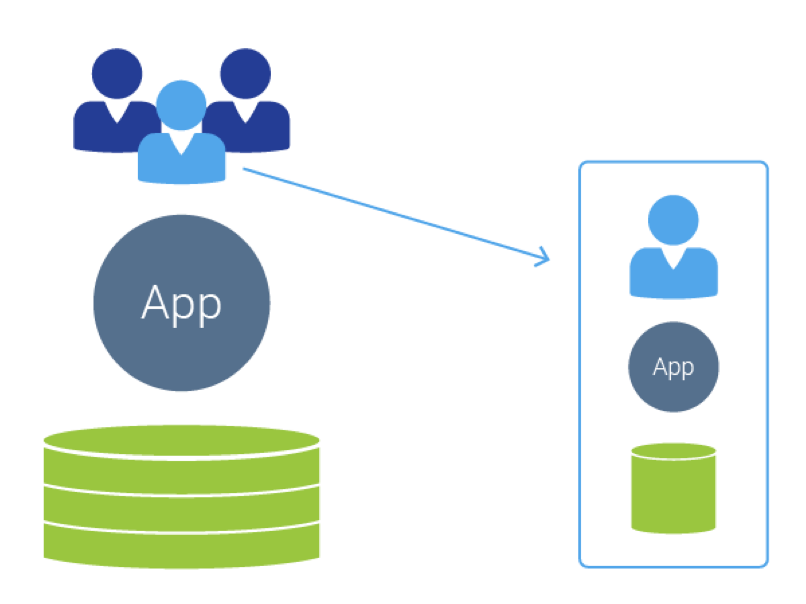
Figure 4: “Can’t we create a separate stack for just this one customer? I promise it’s just this one…” Even a single installation for one “special” customer, breaks the multi-tenant model. Don’t do it.
I would also add that single-tenant (hybrid) cloud applications are worse than on-premise installment. Why? Because they are fake clouds. In single tenancy, each customer has his or her independent database and instance of the software. These instances may reside on the same or different servers. In this model, a customer is, in fact, outsourcing maintenance of their application (software and hardware) to a vendor (or their consultant) that is not likely equipped to perform these tasks. No single vendor in the EHS software industry is large enough to undertake maintenance of the single-tenant infrastructure on behalf of their customers regardless of how inexpensive hardware or software virtualization may be. Even if they offer their hosting on Microsoft Azure Cloud or Amazon Web Services (AWS), they still cannot guarantee multi-tenancy as these solutions address only hardware challenges.
The Economist magazine in 2004 described it: “Those forerunners also promised a software revolution by hosting the software applications of companies. But they failed because they simply recreated each client’s complex and unwieldy datacentre in their own basements, and never overcame the old problems of installation and integration with other software. With each new customer, the old ASPs had, in effect, to build another datacenter; there were few economies of scale.”
To improve their position in a shifting marketplace, on-premises EHS vendors have found a way to market their solutions as “cloud-based” when they are not backed by the fundamental principle of what that means. Considering the large investment that is associated with the purchase or licensing of EHS software, it is critical for customers to be able to tell a true cloud product from a fake one. But how can you spot a fake?
Just ask the EHS software vendor these four questions:
If the answer to any of these questions is yes, the vendor is not committed to only multi-tenant architecture, and you should not move to their “cloud.”
Multi-tenancy is the only proven SaaS delivery architecture that eliminates many of the problems created by the traditional software licensing and upgrade model where software is installed as a single-tenant application on a customer’s premises or at a customer’s or vendor’s data center. In contrast, in multi-tenancy, all customers access the same software on one or a set of linked servers.
Multi-tenancy requires a new architectural approach. Companies have to develop applications from the ground up for multi-tenancy. Once companies commit their limited financial resources to one architecture, it becomes nearly impossible for them to switch to the multi-tenancy model, no matter how many resources they have available. Moreover, for this reason, I am skeptical that many current vendors will be able to make a switch to multi-tenancy fast enough.
A vendor who is invested in on-premise, hosted, and hybrid models cannot commit to providing all the benefits of a true SaaS model due to conflicting revenue models. Their resources are going to be spread thin supporting multiple versions rather than driving innovation. Additionally, if the vendor makes the majority of their revenue selling on-premise software, it will be very difficult for them to fully commit to a true SaaS solution since the majority of their resources will be allocated to supporting the on-premise software.
And if they suddenly introduce a “multi-tenant” model (after selling an on-premises version for 10+ years) who in the world would want to migrate to that experimental cloud without putting the contract out to bid to explore a switch to well established and market-tested true multi-tenant providers? Even Google and Microsoft are playing a catch-up game with Amazon’s AWS when it comes to cloud hosting business. The first mover advantage when it comes to multi-tenancy is a huge advantage for any vendor.
In summary, an EHS software vendor can be either truly multi-tenant or not. If a vendor has installed their software on somebody’s else hardware and runs multiple instances of that software (even if the code base is the same) they are not and will never be true multi-tenant.
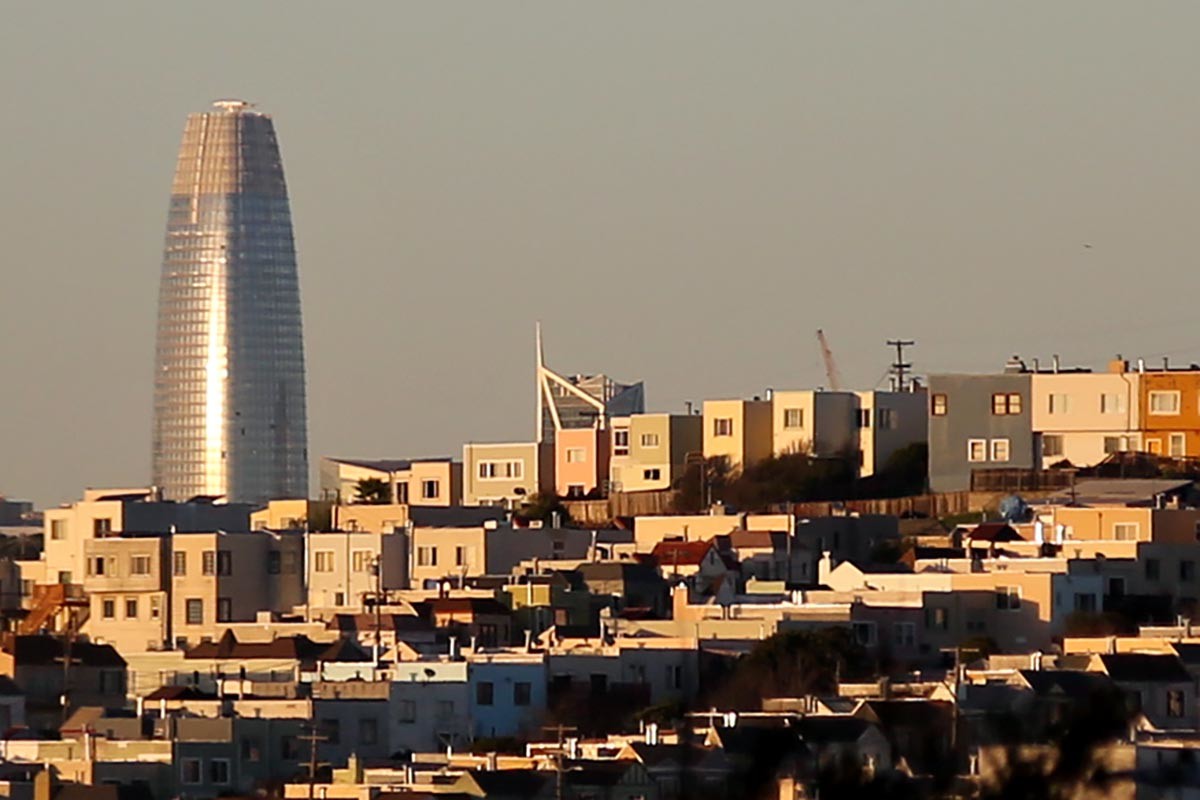

Figure 5: Where do you want your software to reside? In multi-tenant or single -tenant infrastructure? If multi-tenancy is attempted on old infrastructure or legacy application upgrade watch out. After vendor built the first few floors of that skyscraper, there is no easy way to replace the foundation. You will be lucky if they end up like the tower of Pisa or Millennium tower in San Francisco. To keep the tower alive they will have to do constant underpinning of the foundation and restrict access to the structure. And you, the customer, will pay for it. That is what many customers of single-tenant EHS vendors are facing today.
Therefore, when considering a SaaS solution, make sure that the vendor is a true SaaS vendor who is solely committed to the multi-tenant SaaS delivery model and has invested in a true multi-tenant platform. This is the only way to reap all the benefits that a SaaS model has to offer.
IoT is considered one of the fastest growing trends in technology and has a potentially huge impact to automate how we manage water quality, air emissions and other key environmental performance indicators for data monitoring.
As most people researching EHS software know, the words “configurable”, “multi-tenant”, and “platform” are being discussed everywhere. There are plenty of other great discussions on Platform as a Service (PaaS) and multi-tenancy. Let’s look at some tips for getting the most out of configurable software.

A key question to ask (as soon as you start thinking about configurable software) is “what sets my company apart?” What special challenges or circumstances make your EHS needs more nuanced or complex?
These are just a few of the things that could set EHS customers apart. The more unique or specialized tracking and reporting needs you have, the more you will value the ability to have software easily configured for requirements that are typically not supported in “off-the-shelf” solutions.
Most modern software handles the “basics” very well, but when you have unique or emerging needs—including future needs that you don’t even know about yet—having a configurable option really pays off.
When needs change, configurable software can be updated easily and quickly by the vendor or even your own in-house staff, saving time and avoiding the agony of “waiting for the next release”. And, best of all, those changes can be done by trained configuration staff, without the need for software developers and the cost and time usually associated with software development.
Learning and internalizing industry best practices, a hallmark of the EHS professional association NAEM and its outreach events, can help any software buyer make better choices and evaluate software features, platforms, and key differentiators. Check out the excellent library of resources, including publications, newsletters, and webinars from industry peers. By taking advantage of shared industry knowledge, you can dramatically streamline and expedite your search for the right solutions.
One word of caution: many industry publications can be influenced by sponsors. This is not only true in the EHS domain, but in all industry expert reviews. That’s why actually talking and comparing notes with industry colleagues is an invaluable resource to get beyond the reviews and hear about real-life experiences with the EHS domain itself and the software options that others have actually used.
If you’re looking for advice on how configurable software may be used to address your EHS needs, talking to actual software users will help. Locus, along with many other vendors and hundreds of EHS professionals, routinely attends NAEM’s EHS and Sustainability Software and Data Management Conference in order to meet with potential customers and dive into any questions you may have.

“Configurable” means something different to each software vendor. Some will say “everything is configurable”—for a price. Others will tell you that you can change report names and add a few fields to outputs, and they call this being “configurable”.
Ask the vendor to explain in detail exactly what can easily be configured—and what is “off limits” and requires actual development effort (i.e., additional cost). You might ask:
By knowing the software’s limitations, you can make better choices on the best fit for your current (and future!) needs. Your software vendor may also identify new configurable features that you hadn’t considered before, but that would greatly improve the usability of the software. Even if you don’t need these options now, knowing you have access to them in the future is critical when selecting software.

As we’ve established, “configurable” software can mean anything—from a total blank slate and empty platform, to changing a title of a single data entry field, and everything in between. A “blank slate” may excite more technical people who love to tinker in software programs. For others, the thought of building their software from the ground up might elicit general fear and discomfort.
Most customers want something off-the-shelf that perfectly meets their needs. Honestly, who can disagree? That is the gold standard and what everyone wants. In reality, this solution is hard to find—especially for customers with unique need—and often the software tools that address those unique needs are so focused on a particular niche that they neglect some of the other, more basic EHS needs you might have.
The good news is that configurable software provides almost unlimited options for customers, and it can make a huge difference in how the software fits into your EHS workflow. With some solutions on the market today, you could choose to build one application from a blank slate and make minor tweaks to another pre-built application in the same software.
One of the common pitfalls that EHS professionals frequently encounter in selecting a software solution for a specialized need is the tendency to narrow their options down to limited set tailored to their specific industry. For example, if your organization has requirements for refrigerant handling, you might feel constrained to selecting a solution with specific “out-of-the-box” capabilities for that need. Considering the configurability of the software may allow you to consider new and more robust options, and some simple configurations to an existing chemical inventory application could address your refrigerant reporting needs even more accurately, within a single EHS platform.
![]()
Many customers will buy existing applications that meet their general needs, but eventually realize they need another form, a mobile solution, or changes for new regulations. Anyone in the EHS industry knows this is the norm rather than the exception.
According to Forbes, federal departments, agencies, and commissions issued 3,853 rules in 2016, while Congress passed and the president signed 214 bills into law—a ratio of 18 rules for every law. That’s just at the federal level. It’s not hard to imagine the amount of change when you factor in state and local rules and requirements.
Over the anticipated implementation life for your EHS software, you can be reasonably assured that the EHS requirements for your organization are going to be changed in some way. Some of these changes you can anticipate, but not all. Given such routine change, you can safely assume that the more configuration options you have, the more prepared you’ll be for those changes. You’ll be in a better position if you know you can configure your software quickly, rather than waiting for a scheduled vendor update that may be out of your control.
Configurable software can be an effective, sustainable long-term management and reporting solution that integrates smoothly into your existing EHS workflows, but it does require you to do your homework.
You can set yourself up for success with some initial reflection and examination of your organization’s unique needs, a few conversations with industry peers, a healthy skepticism of seemingly perfect “out-of-the-box” solutions, and a willingness to ask tough questions of potential software vendors. Think ahead to the future challenges and regulatory changes that might impact your organization, and make sure your potential software vendor has provided evidence that you’ll be able to handle these changes through configuration. Take the time to truly imagine your perfect application and EHS workflow, and ask the vendor to show how it can be possible through configurability. And finally, don’t be afraid to think outside the box!

About guest blogger— Marian Carr, Locus Technologies
Ms. Carr is responsible for managing overall customer solution deployments and customer relationships with Locus’ government accounts. Her career at Locus includes heading the product development team of the award-winning cloud-based environmental ePortal solution as well as maintaining and growing key customer accounts with Locus’ Fortune 100 enterprise deployments. In addition, Ms. Carr was instrumental in driving the growth and adoption of the Locus EIM platform with key federal and water organizations.
299 Fairchild Drive
Mountain View, CA 94043
P: +1 (650) 960-1640
F: +1 (415) 360-5889
Locus Technologies provides cloud-based environmental software and mobile solutions for EHS, sustainability management, GHG reporting, water quality management, risk management, and analytical, geologic, and ecologic environmental data management.
