The Past, Present, and Future of EHS & ESG
To celebrate a milestone 25 years of success in EHS and ESG software development, we sat down with Locus President, Wes Hawthorne for a brief discussion. In this post, we ask him a series of questions highlighting the past, present and future of EHS and ESG.
1. What are the greatest challenges that environmental professionals are facing?
One of the persistent challenges we’ve seen for the past 25 years is that the responsibilities of environmental professionals are continually expanding. Previously, almost all environmental work was localized, with facility-level permits for air, water, waste, etc. That has expanded over the years to include new regulations and reporting requirements for sustainability, social metrics, and other new compliance areas, while the old facility-level programs still continue. This has led to more pressure on environmental managers to keep up with these programs, and increased reliance on tools to manage that information. That’s where Locus has always focused our effort, to make that ever-expanding workload more manageable with modern solutions.
2. What are the most interesting trends in EHS and ESG?
The current flood of interest in ESG is certainly notable as far as bringing corporate attention to the environmental field, as well as having requirements originate from the SEC here in the US. We have become accustomed to managing oversight from multiple regulatory bodies at the local, state, and federal level, but SEC would be a newcomer in our line of work. Their involvement will be accompanied by a range of new requirements that are common for the financial world, but would be unfamiliar to environmental staff.
Across other EHS fields, we are seeing increased demand for transparency in EHS functions. Overall, this is a positive move, as it brings more attention to EHS issues and develops a better EHS culture within organizations. But this also drives the need for better tools to make EHS information readily available across all levels of the organization.
3. What are the most disruptive technologies available today?
As far as technologies, the ones most likely to have significant impact in the environmental field are ones that don’t require a significant capital investment. Although there are definitely some practical advantages to installing smart monitoring devices and other new technologies, procuring the funding for those purchases is often difficult for environmental professionals. Fortunately, there are still many technologies that have already been implemented successfully in other fields, but only need to be adapted for environmental purposes. Even simple changes like using web-based software in place of spreadsheets can have a huge impact on efficiency. And we haven’t yet seen the full impact of the proliferation of mobile devices on EHS functions. We are still working on new ways to take advantage of mobile devices for data collection, analysis, and communication purposes.
4. What do you think are the biggest innovations of the last 25 years in our field?
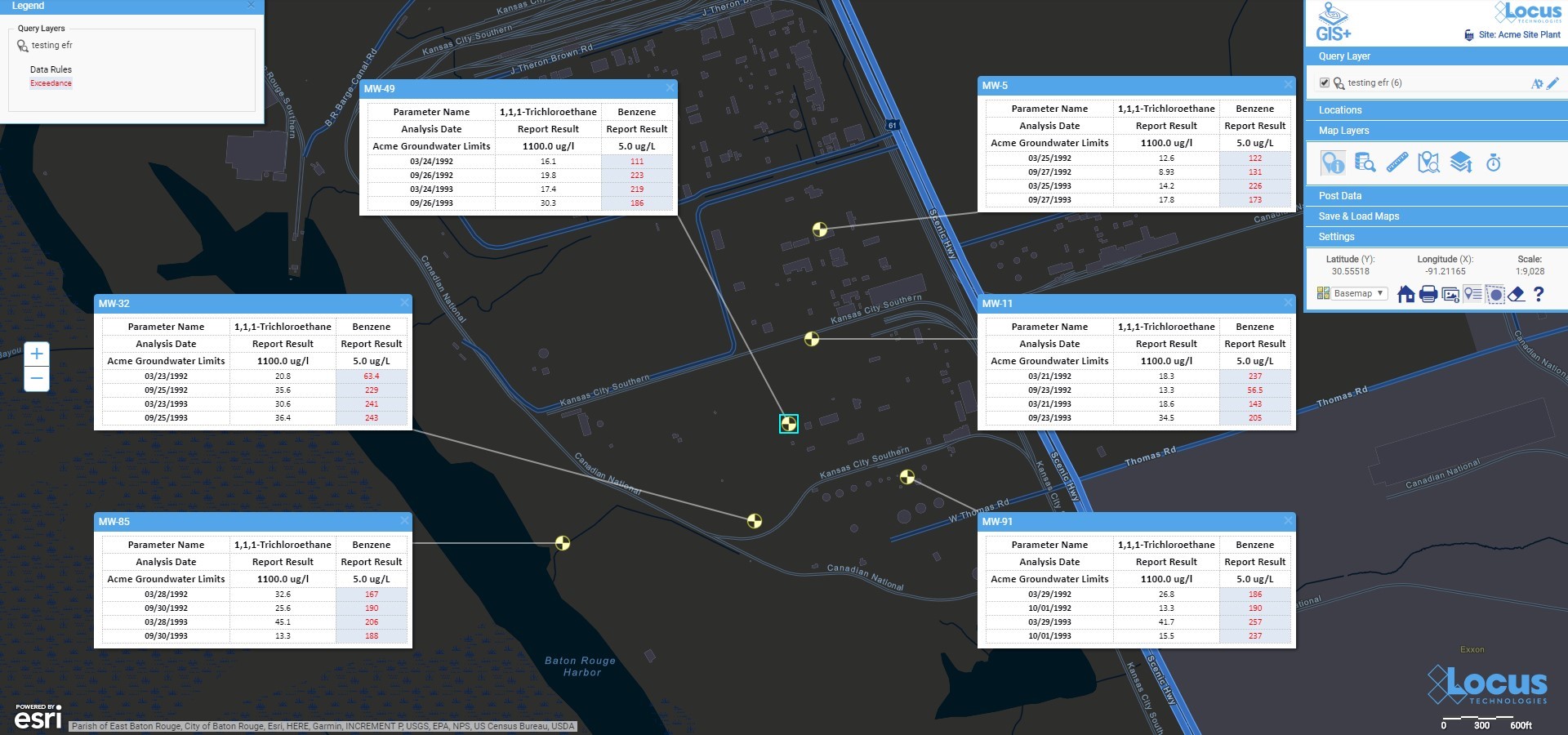
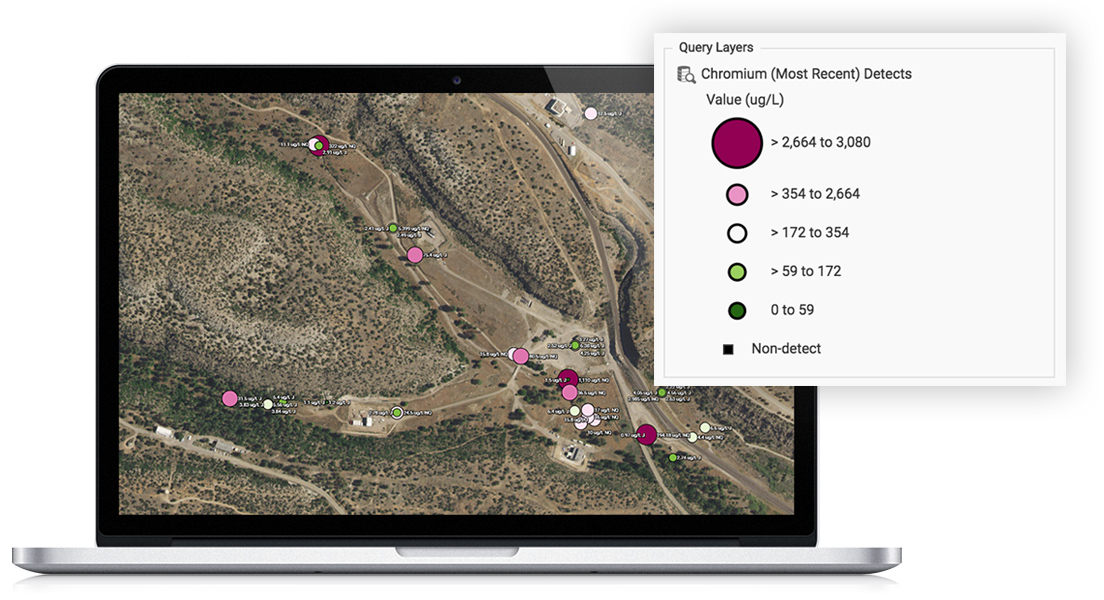
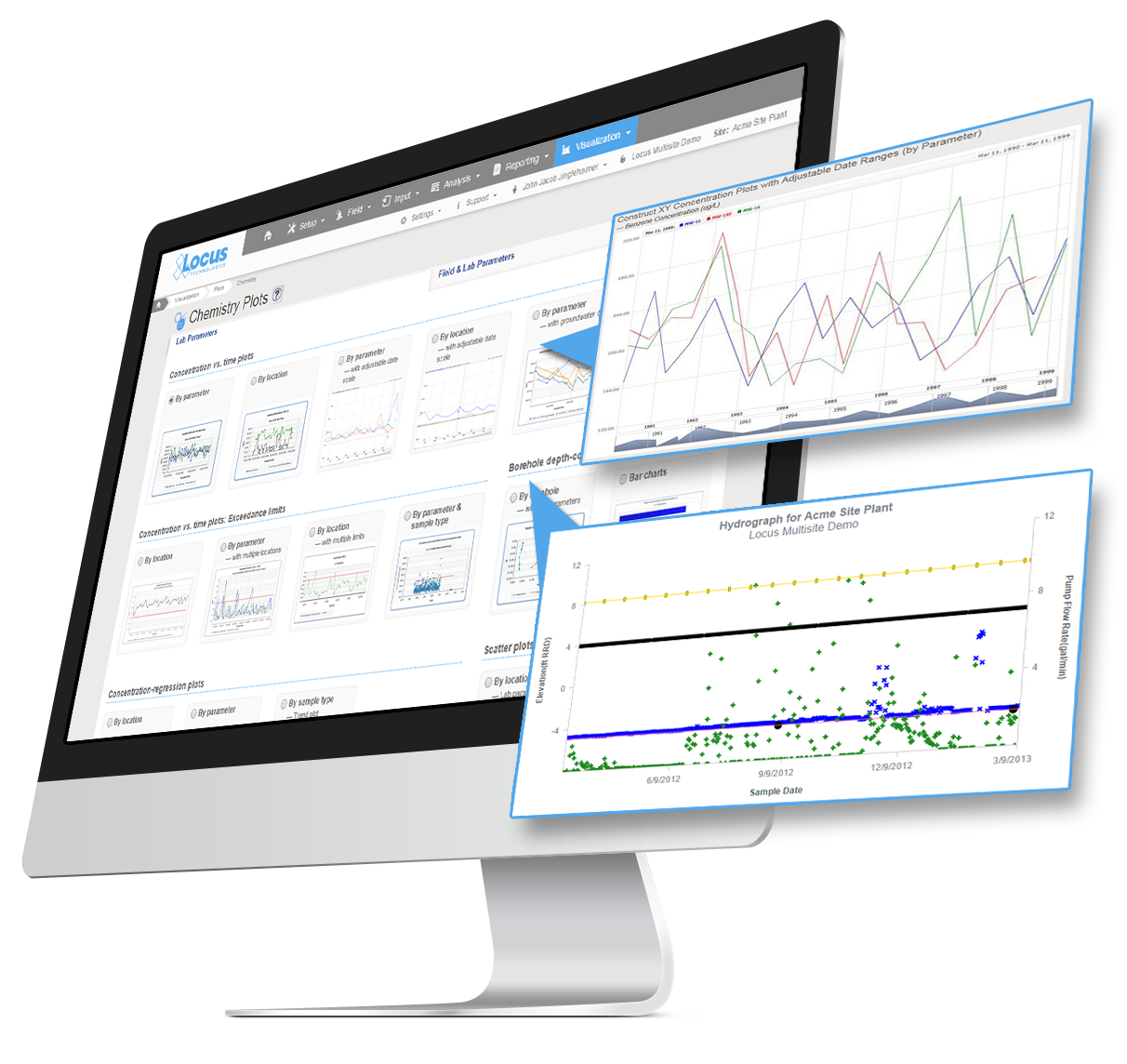
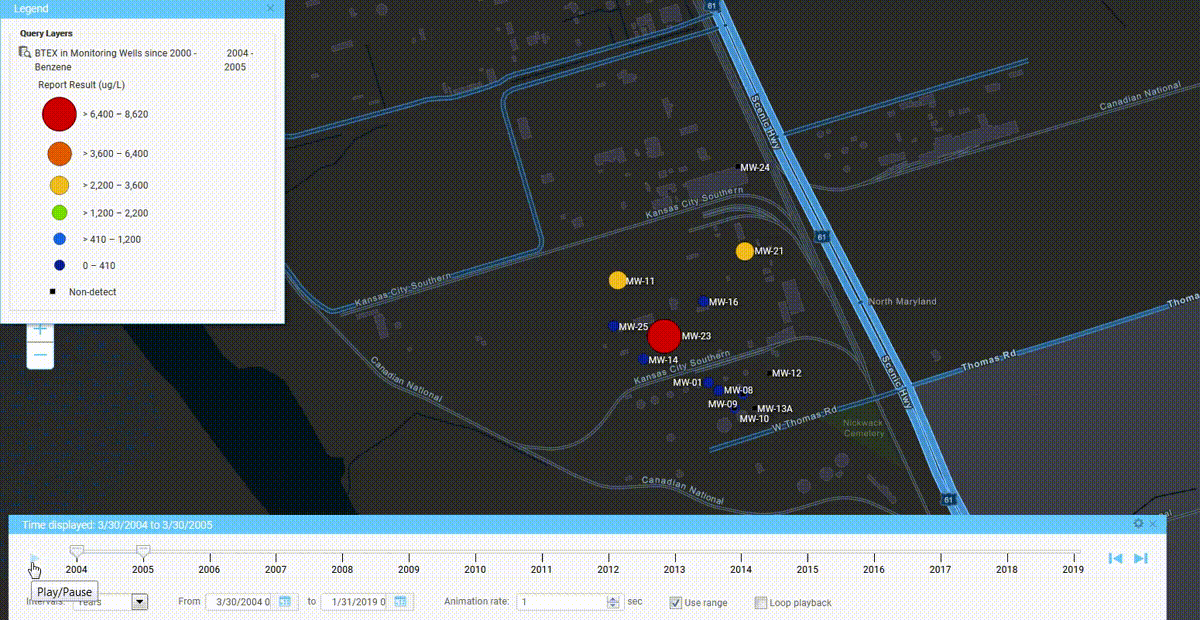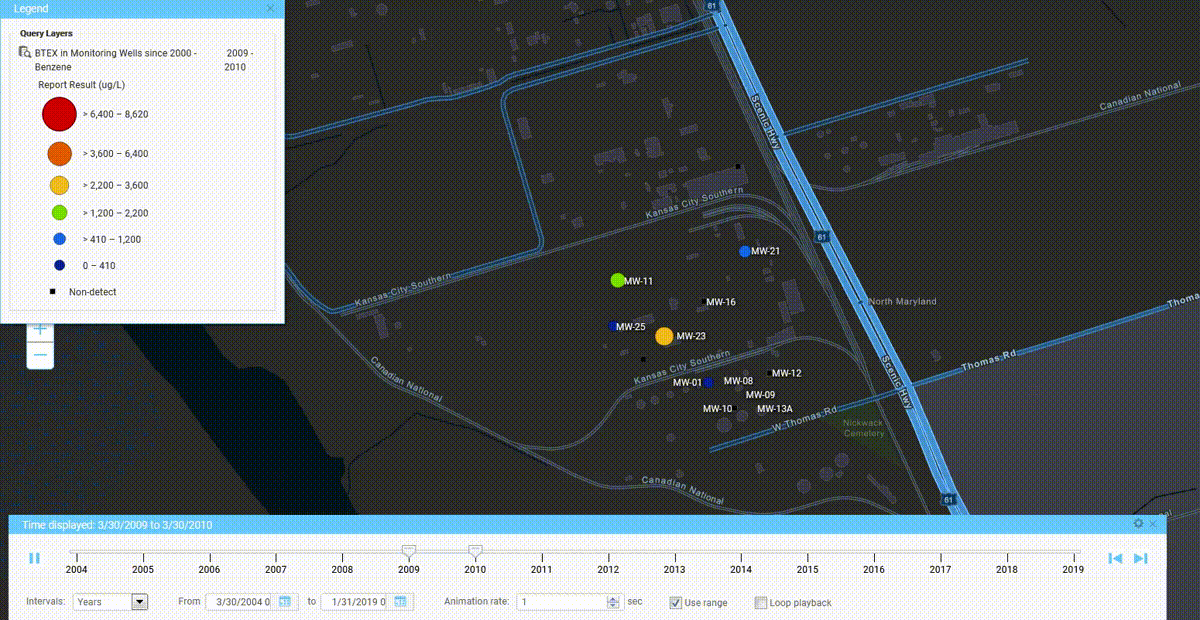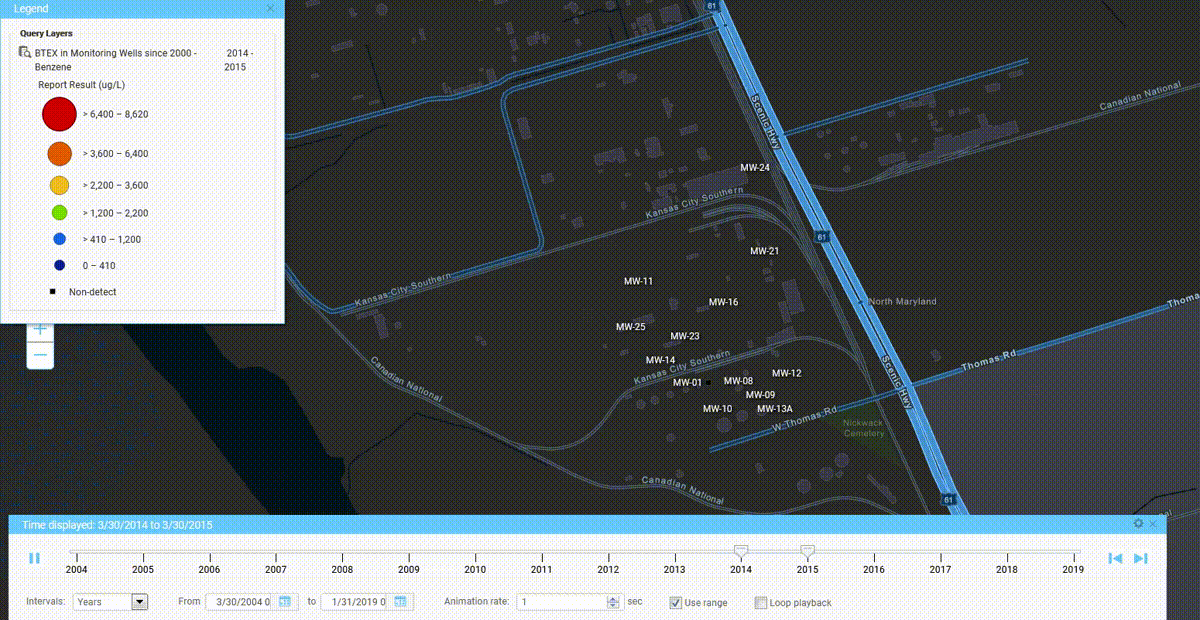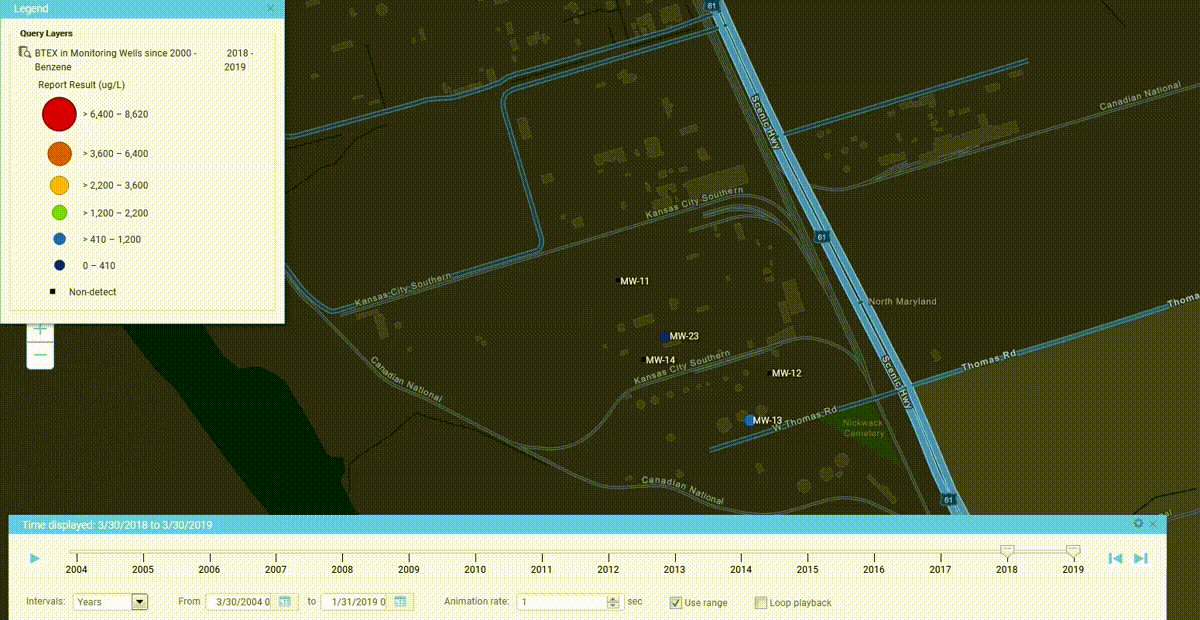
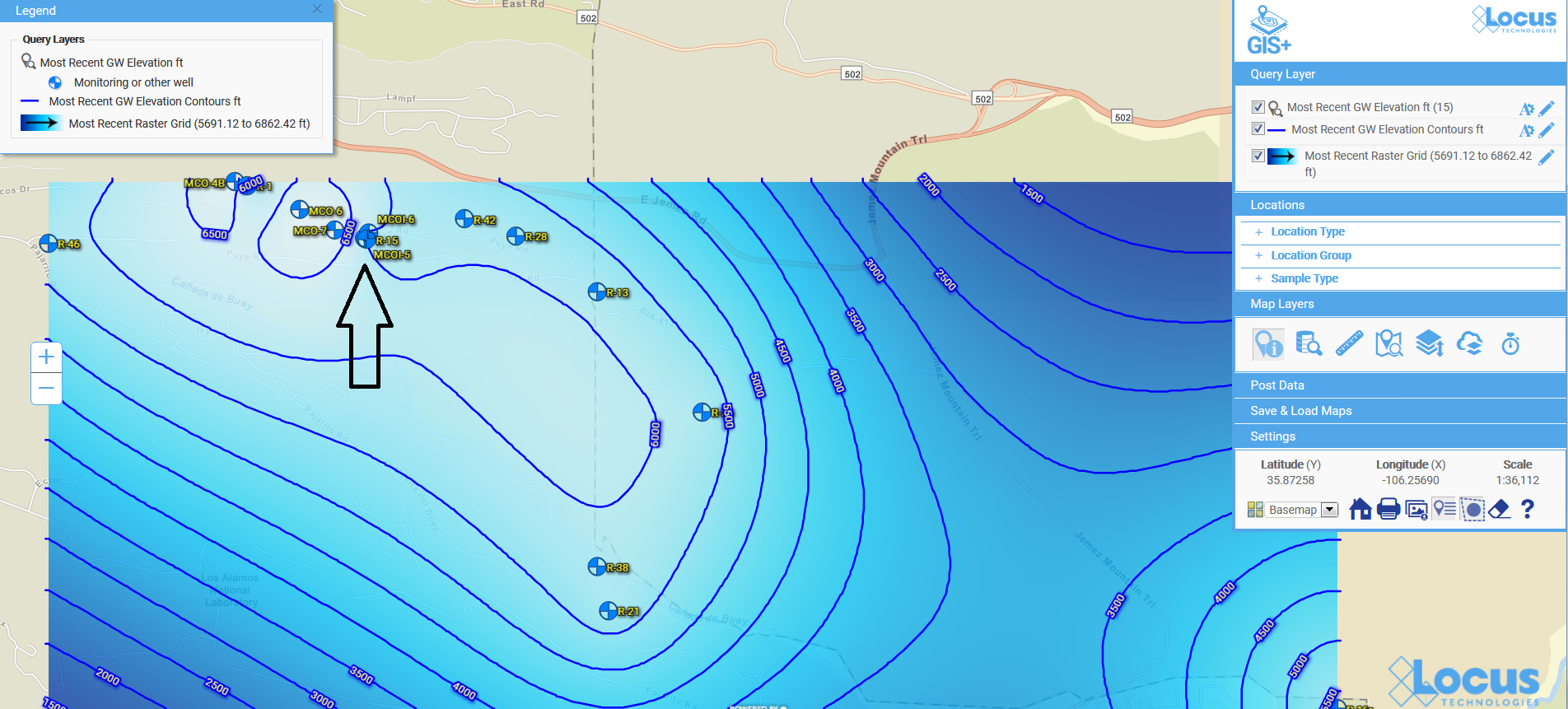
We’ve seen a number of innovation milestones in the past 25 years, and while we didn’t invent SaaS, we’ve been largely responsible for adapting it and perfecting it for environmental purposes. One of the major innovations we’ve integrated into our products include online GIS tools where users can easily visualize their environmental data on maps without expensive desktop software. Another one was our fully configurable software platform with built-in form, workflow, and report builders tailored for environmental purposes, which allows anyone to build and deploy environmental software applications that exactly match their needs. There have been many other innovations we’ve incorporated into our software, but these two stand out as the most impactful.
5. Where do you see Environmental and ESG reporting in the future?
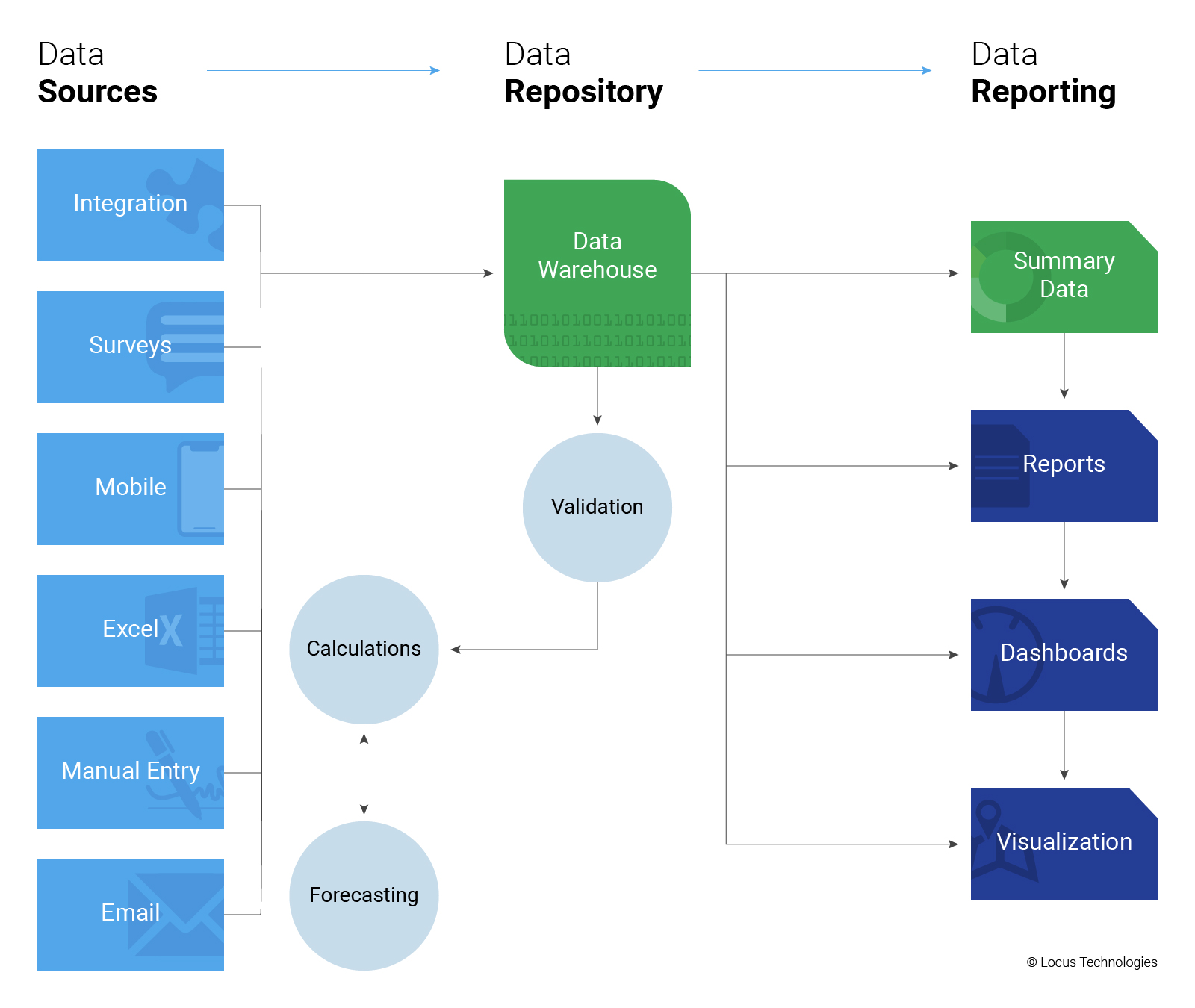
More and more, we are seeing all types of reporting being converted into pure data exchanges. Reports that used to include regulatory forms and text interpretations are being replaced with text or XML file submittals. This transition is being driven largely by availability of technology for EHS professionals to generate and read these files, but it is also promoted by regulatory agencies and other stakeholders receiving these reports. Stakeholders have less time to read volumes of interpretive text, and are becoming more skeptical of potential bias in how facts are presented in text. These are driving the need for more pure data exchanges, with increasing emphasis on quantifiable metrics. These types of reports are also more readily compared against regulatory or industry standards. For reporters, lengthy corporate reports with volumes of text and graphics are becoming less common, and the success of an organization’s programs will be increasingly reliant on robust data sets, since ultimately only the data will be reported.
6. What has been the key reason for Locus’ success for the past 25 years?
There are actually a few that immediately come to mind. One reason is the nature of our continually evolving products. By providing our solutions as SaaS, our software adapts with new environmental requirements, and with new technologies. If our software was still the same as it was 25 years ago, it simply wouldn’t be sufficient for today’s requirements. Since our software is updated multiple times each year, it is difficult to notice the incremental changes, but they can be readily seen if you compare today’s software with the original in 1997. And we’re committed to continuing the development of our products as environmental needs change.
The other primary reason for our success is our excellent staff and the environmental expertise we bring to our customers. We simply could not provide the same level of support without our team of environmental engineers, scientists, geologists, chemists, and an array of others. Having that real-world understanding of environmental topics is how we’ve maintained customer relationships for multiple decades. And our software only has value because it is maintained and operated by staff who appreciate the complexity and importance of environmental work.
 Mr. Hawthorne has been with Locus since 1999, working on development and implementation of services and solutions in the areas of environmental compliance, remediation, and sustainability. As President, he currently leads the overall product development and operations of the company. As a seasoned environmental and engineering executive, Hawthorne incorporates innovative analytical tools and methods to develop strategies for customers for portfolio analysis, project implementation, and management. His comprehensive knowledge of technical and environmental compliance best practices and laws enable him to create customized, cost-effective and customer-focused solutions for the specialized needs of each customer.
Mr. Hawthorne has been with Locus since 1999, working on development and implementation of services and solutions in the areas of environmental compliance, remediation, and sustainability. As President, he currently leads the overall product development and operations of the company. As a seasoned environmental and engineering executive, Hawthorne incorporates innovative analytical tools and methods to develop strategies for customers for portfolio analysis, project implementation, and management. His comprehensive knowledge of technical and environmental compliance best practices and laws enable him to create customized, cost-effective and customer-focused solutions for the specialized needs of each customer.
Mr. Hawthorne holds an M.S. in Environmental Engineering from Stanford University and B.S. degrees in Geology and Geological Engineering from Purdue University. He is registered both as a Professional Engineer and Professional Geologist, and is also accredited as Lead Verifier for the Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Low Carbon Fuel Standard programs by the California Air Resources Board.