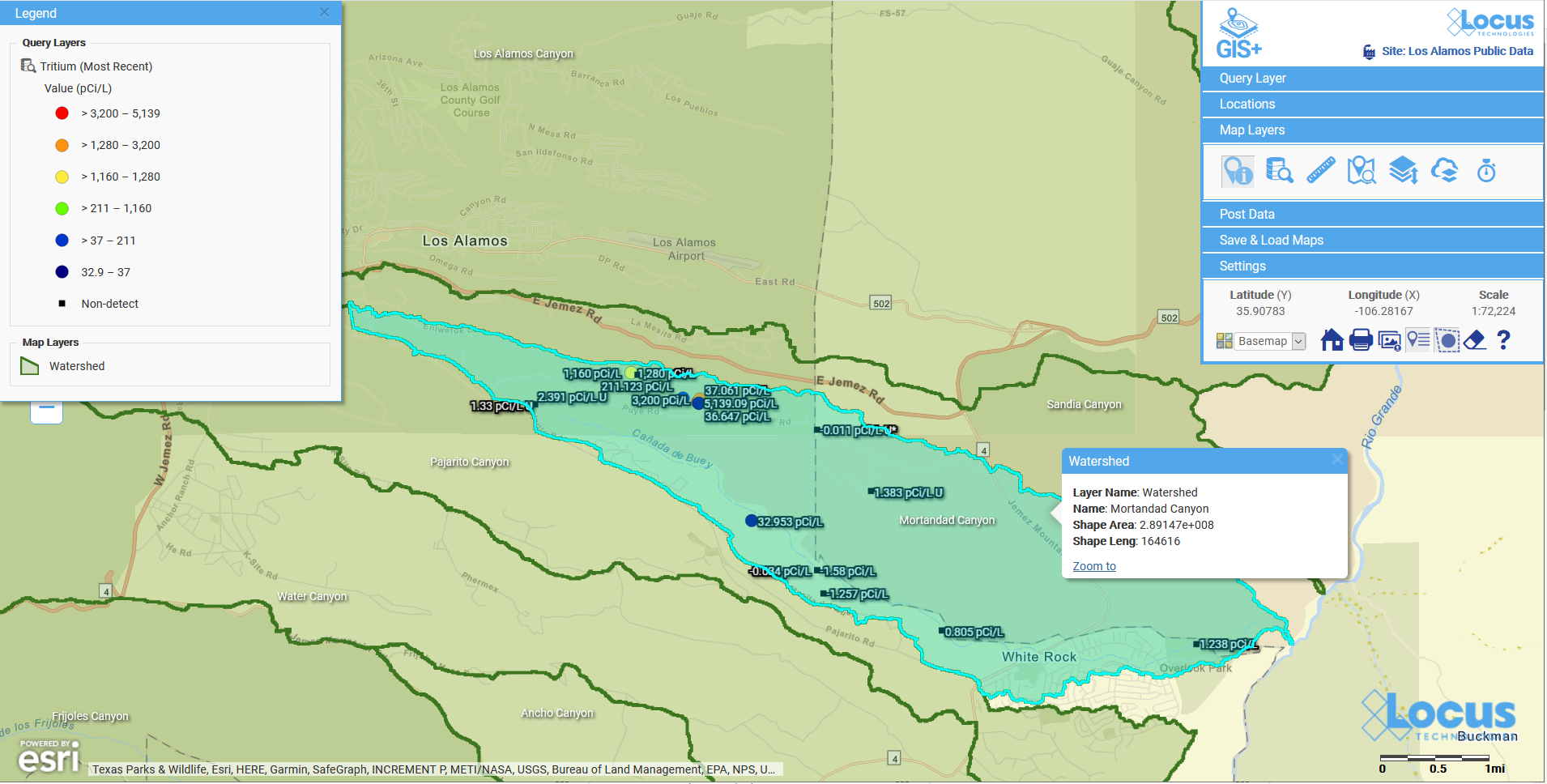
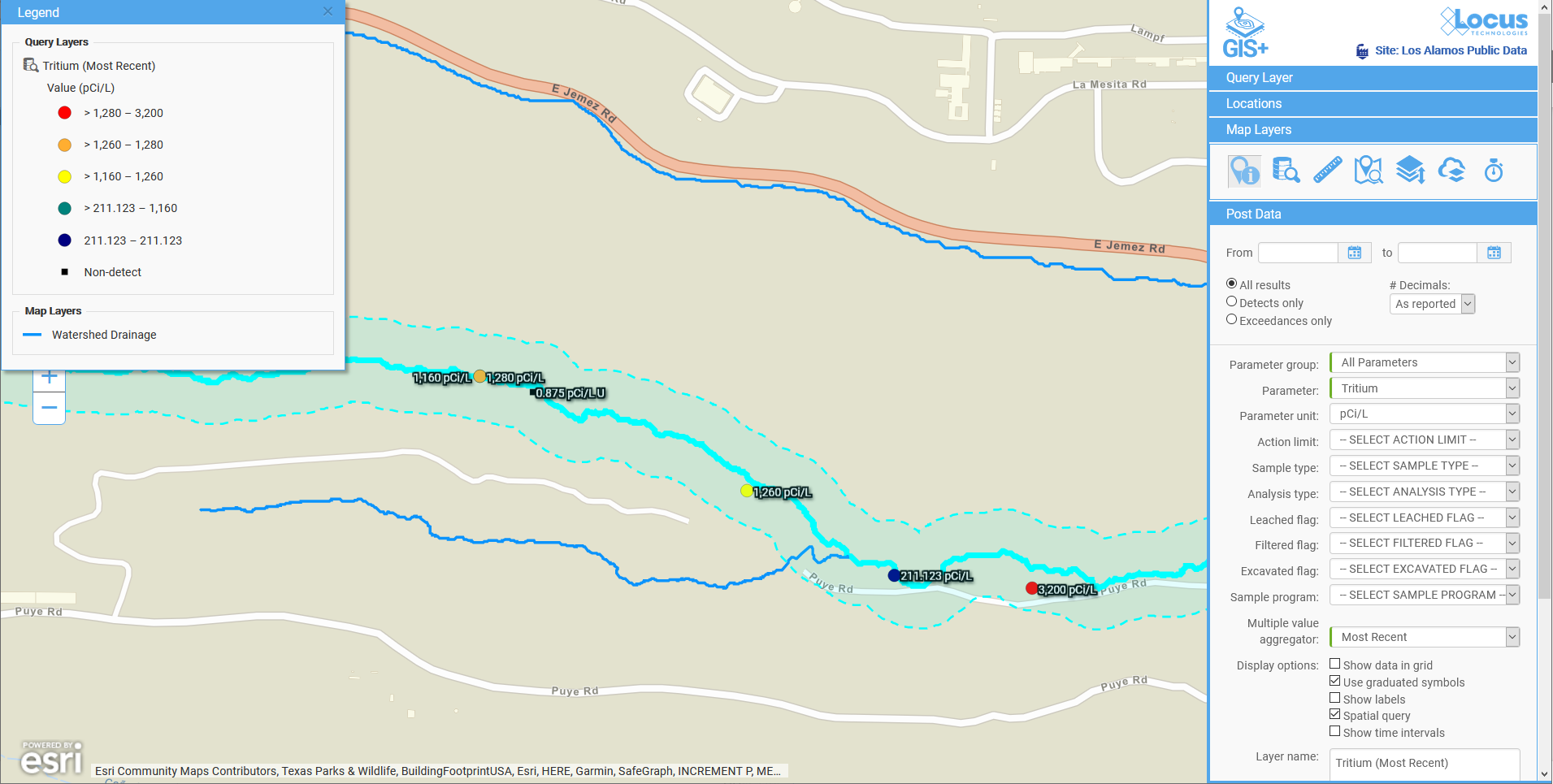
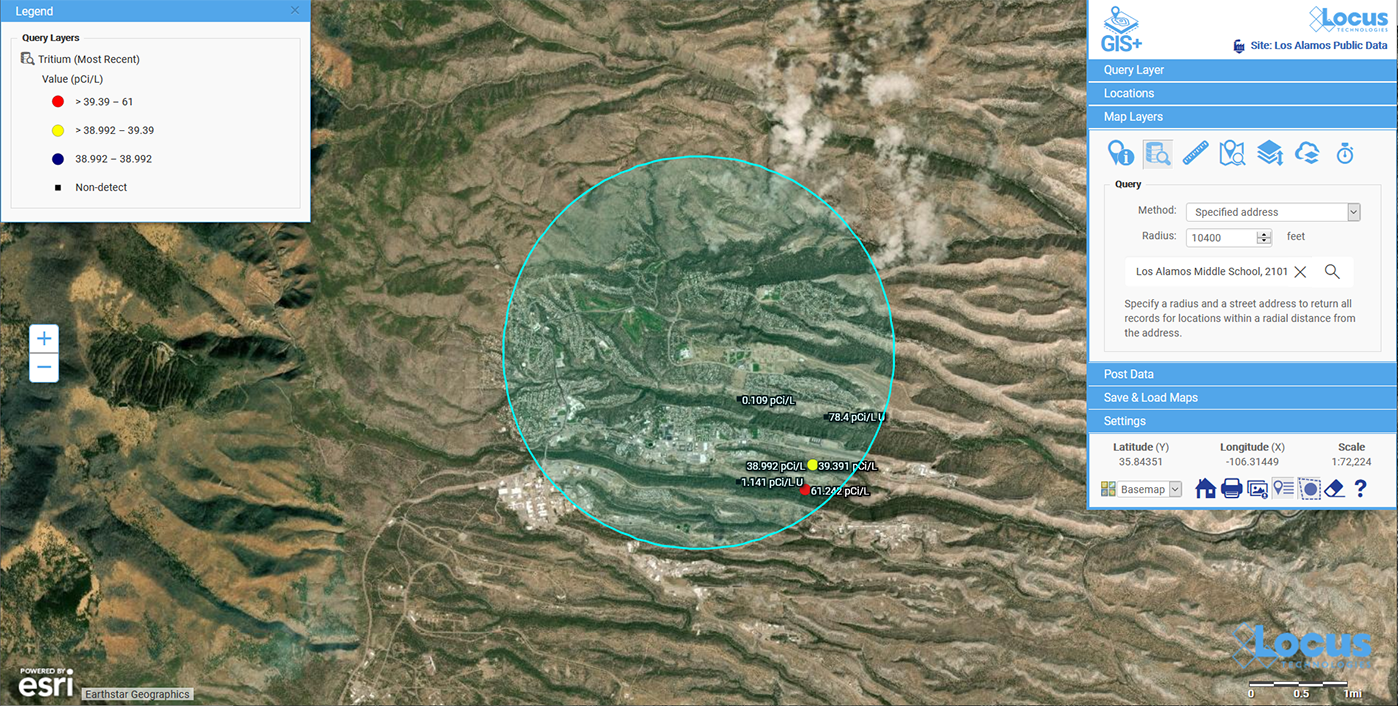
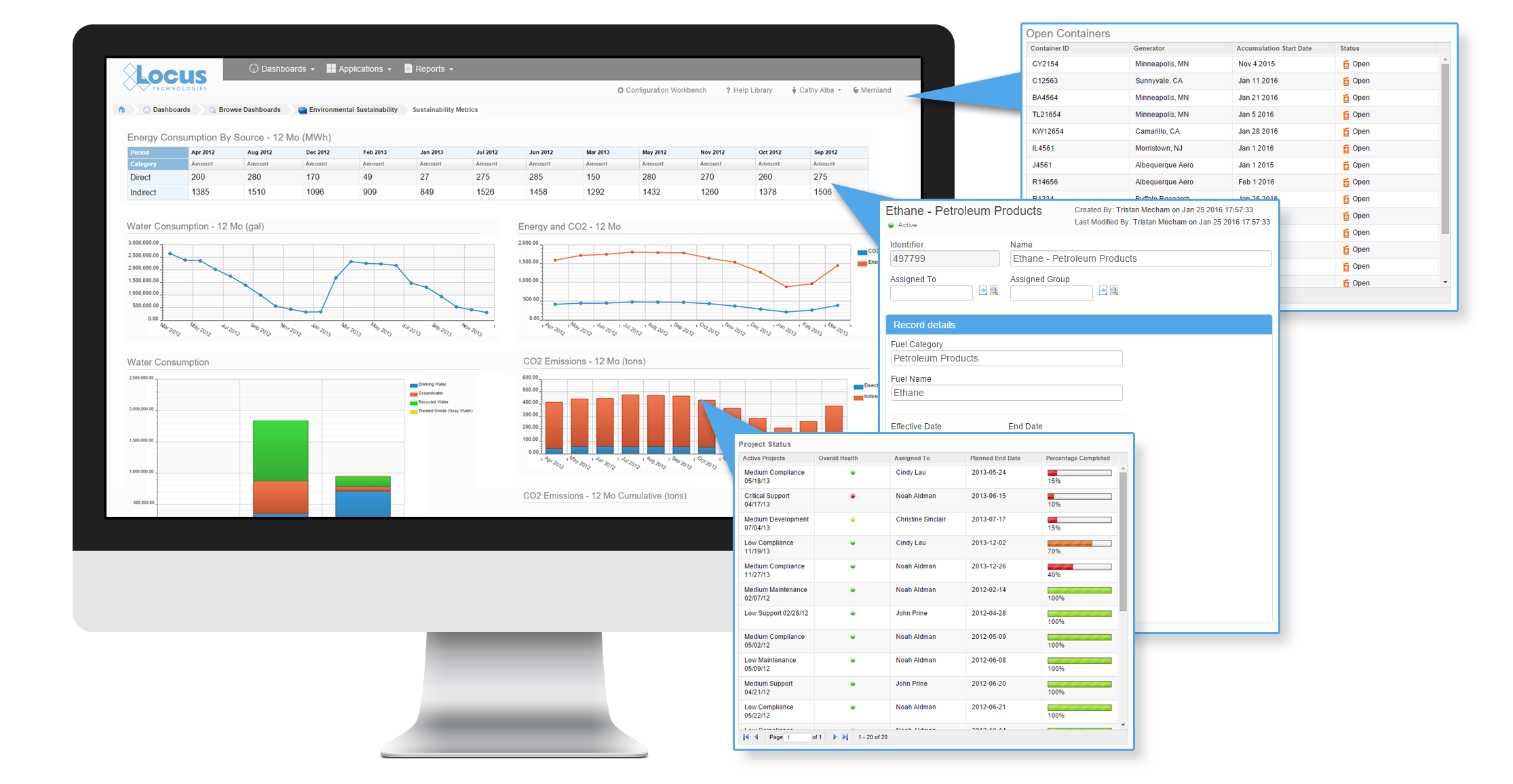
Q&A with the Locus Support Team
The biggest differentiator between Locus and other EHS software providers is our support team. Not only do we pride ourselves on the quickest and most efficient resolutions in the industry, but on our human approach to support. Get to know our support team as we recently sat down (virtually) with them to talk about the ins and outs of their field, how it is working for Locus, and more.
What is your most common support case?
Our most common support case is user management related. Many times, our customers need assistance adding new users or updating their user lists. We receive a lot of requests for resetting passwords.
What is the most unique case you’ve seen?
Almost ten years ago, there was a bug within SQL itself! It was quite a mystery. We would venture to say that we have at least one unique case every week. No single case is the same! It certainly keeps us on our toes. We also had a case once where an organization was acquired by another organization. Due to this, we had to rename the users and organizations which ended up resulting in over 300 user changes which impacted historic records.
What is your average response time?
It is our policy to respond to all cases within two hours of receiving them (given that they come in between the hours of 5am and 3pm Pacific Time). If they come in outside of those hours, we respond within 2 hours of beginning our normal hours. We get many compliments on how speedy our response times are! It is the policy of the team for Tier 1 staff members to check new cases every thirty minutes or so. Critical issues typically receive almost immediate responses! Quick response times are one of our proudest achievements.
Can you name a case that made a great impact on the user?
We have had many cases where we have received numerous thank yous from the customer. There has been a time or two when a customer did a widespread data update without meaning to. Our quick response and ability to revert their changes was much appreciated. We have also been known to help our customers with some very interesting issues that require quite a bit of troubleshooting on our end. The Support Team is incredibly patient and willing to dive deep into questions that customer’s come to us with.
What is something people may not know about the support team?
The Locus Support Team consists of many individuals from a variety of backgrounds ranging from Environmental Engineering, Biology, Environmental Science, Environmental Health and Safety, Mathematics, Data Management, GIS, and much more! The Tier 1 team consists of three outstanding individuals who work across the Support Team, Engineering Team, and Configuration team. The Tier 2 team consists of a wide variety of developers, configurators, and specialists in the field. Together, the Locus Support team has over 75 years of combined experience in the Environmental field. We have a few folks on the team that have outward appearances outside of the norm ranging from long hair, piercings, tattoos, and even purple hair.
How has working more hours remotely affected your team?
Because our team is spread across the United States, with team members working out of the Asheville and Mountain View offices, as well as remote employees, we haven’t been impacted as much by the stay at home COVID-19 orders. Our team has always excelled at communication through email and other online chat services. The ability to talk through tools such as Teams and Skype, has given us the advantage edge during this pandemic. In addition, a large number of our Support Team are remote employees ranging across California, Tennessee, Indiana, Utah, and many other states.
What is your favorite part about working on the Locus support team?
The first answer that came to the team was that we are all a family! We are incredibly supportive and encouraging of one another and we have FUN while working! One of the fun things that we all have in common is our deep–rooted love for animals. One of our favorite pastimes is sharing pictures of our animals, as well as their silly antics! We also like to share about our parenting concerns, particularly during COVID-19 times! Locus is an amazing place to work, in part because of the educated, experienced and awesome personalities we have working as a WHOLE team, rather than just a support team. When asked, the number one response was the friendly and family-like atmosphere.
What certificates/degrees does the support team hold?
Master of Applied Science
- Environmental Policy and Management
- Environmental Engineering
- Biology
Associate’s
- Crisis, Emergency and Disaster Management
- Emergency Management
Bachelor of Science
- Environmental Science
- Environmental Chemistry
- Civil Engineering
- Physical Geography
- Mathematics
- Integrated Science and Technology
Certifications
- FEMA Certifications
- ISO 9001, 9000 and 14000 Internal and Lead Auditor Certification
- Accredited GHG Verififier
- 40-hr HazWoper
- Graduate certificate in GIS
[sc_button link=”https://www.locustec.com/services/technical-support-training/” text=”More on Locus Support” link_target=”_self” centered=”1″]